Understanding the differences between materials can be a challenge, especially when it comes to zirconium silicate and its alternatives. Decision-makers often face the dilemma of choosing the right material based on performance and cost-effectiveness. This article addresses that concern by showcasing various comparative studies assessing the efficacy of zirconium silicate against other options. By providing clear insights and data, this article will help you make informed choices that benefit your project and organization. Rest assured, this guide is built on credible research and expert opinions.
How Are Comparative Studies Conducted on Zirconium Silicate?
The integrity of any research lies in its methodology, and comparative studies on zirconium silicate are no exception. First and foremost, understanding how these studies are structured provides clarity on their findings. Researchers typically establish a set of criteria to evaluate zirconium silicate against competing materials. This includes aspects like durability, thermal resistance, and cost.
Key metrics utilized in these studies often include mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. These measurements allow for a straightforward comparison. Moreover, the sources of data play a vital role, encompassing laboratory tests, real-world applications, and expert analyses.
Another crucial factor is sample size. Larger sample sizes improve the reliability of results, reducing the margin for error. Therefore, when reviewing these studies, look for those that mention significant sample sizes to ensure their conclusions are robust.
In essence, every aspect of how these studies operate—from the chosen metrics to the volume of data—affects how we perceive zirconium silicate’s efficacy. Awareness of these factors can guide B2B professionals in making informed decisions.
| Metrics | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Resilience under stress | Determines durability |
| Thermal Stability | Resistance to high temperatures | Prevents material failure |
| Chemical Resistance | Reaction to chemicals | Ensures longevity |
| Sample Size | Number of tests conducted | Improves reliability |
What Are the Main Advantages of Zirconium Silicate?
Zirconium silicate offers several advantages that appeal to industries looking for reliable material solutions. For instance, its exceptional durability makes it a strong contender for many applications. Its ability to withstand high temperatures and resist wear allows it to perform under demanding conditions, often outperforming traditional materials.
Tracking its performance, case studies have shown that zirconium silicate maintains integrity in harsh environments, making it particularly valuable in sectors like construction and manufacturing. Additionally, its low thermal expansion means it is less likely to warp, ensuring precision in applications like dental prosthetics.
Beyond durability, zirconium silicate is chemically inert. It does not react with many substances, which enhances its longevity and reduces maintenance costs. Moreover, its aesthetic appeal makes it ideal for use in consumer products where appearance matters.
Here are some specific advantages of zirconium silicate:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower long-term operational costs due to durability.
- High Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Offers substantial strength without excessive weight.
- Versatile Applications: Useful across varied sectors, from dental to industrial settings.
- Low Maintenance Needs: Less frequent replacements reduce hidden costs.
Overall, these characteristics make zirconium silicate not just a robust option but also a cost-effective one in the long run.

The image illustrates zirconium silicate used in dental and construction applications, highlighting its versatility.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Durability | Withstands wear and tear |
| Low Thermal Expansion | Maintains shape under temperature changes |
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive with most substances |
| Aesthetic Appeal | Visually appealing for consumer use |
What Are the Common Alternatives to Zirconium Silicate?
While zirconium silicate boasts numerous strengths, it’s worth evaluating common alternatives as well. For example, materials such as alumina and silica are frequently used in similar applications. Each comes with unique properties and capabilities.
Alumina, or aluminum oxide, is often regarded for its hardness and thermal stability. However, it may not have the same aesthetic qualities as zirconium silicate. In contrast, silica is favored for its light weight and cost, but it typically falls short in terms of durability and chemical resistance.
Another alternative is ceramic-based materials. While they can be stronger in certain scenarios, they may lack the versatility of zirconium silicate.
When considering alternatives, keep these factors in mind:
- Performance Requirements: Ensure the alternative meets application needs.
- Cost-Benefit Analysis: Evaluate long-term financial implications.
- Availability and Sourcing: Check how readily available the materials are.
- Environmental Impact: Consider sustainability factors in material sourcing.
As you compare these options, consider the specific needs of your project. The right choice will depend on factors such as cost, performance standards, and environmental conditions.
| Alternative Material | Key Features | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | Hard, thermally stable | Less visually appealing |
| Silica | Lightweight, cost-effective | Lower durability |
| Ceramic | Extremely strong | Less versatility |
What Do Comparative Studies Say About Cost-Effectiveness?
Cost-effectiveness is paramount when evaluating materials. In multiple comparative studies, zirconium silicate often emerges favorably in terms of both initial investment and long-term savings.
These studies typically analyze initial costs, maintenance expenses, and lifespan. While zirconium silicate may have a higher upfront price compared to some alternatives, its durability and low maintenance requirements often lead to lower operational costs over time.
For example, in industries where equipment durability impacts revenue—such as in manufacturing—investing in a more expensive material like zirconium silicate may yield better financial performance. Case studies have shown reductions in downtime and maintenance expenditures associated with its use.
In conclusion, assessing cost-effectiveness requires examining not only the purchase price but also the overall return on investment. Decision-makers should consider long-term implications and potential savings when evaluating zirconium silicate against alternative materials.
- Evaluating Long-term Costs: Look beyond the initial price to gauge true value.
- Estimating Maintenance Needs: Factor in costs for upkeep and replacements.
- Analyzing Impact on Production: Recognize how material choice affects operational efficiency.
- Consideration of Downtime Costs: Account for potential losses during maintenance.
How Do Performance Metrics Influence Material Choice?
Understanding performance metrics is critical when selecting materials. These metrics help professionals like you identify which material meets the specific requirements of your project.
Key indicators include strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance, among others. For instance, in situations demanding high tensile strength, zirconium silicate often stands out for maintaining integrity under stress, making it suitable for construction purposes.
Flexibility is another important measure. While some materials can crack under pressure, zirconium silicate’s resilience means it’s less likely to face such failures.
Thermal resistance also plays a significant role. For applications involving extreme temperatures, materials that can withstand heat without degrading are essential. Here, zirconium silicate excels, making it a preferred choice in sectors like aerospace and automotive.
When evaluating materials, prioritize these performance metrics based on your specific needs. Understand how each one may impact the longevity and effectiveness of your chosen solution.
| Performance Metric | Importance | Zirconium Silicate’s Strength |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Determines ability to withstand stress | High |
| Flexibility | Assesses material adaptability | Excellent |
| Thermal Resistance | Evaluates heat sustainability | Superior |
What Role Do Industry Standards Play in Efficacy Comparisons?
Industry standards serve as a foundation for understanding material performance. They establish benchmarks that materials must meet to be considered reliable and safe.
For zirconium silicate, adherence to these standards assures end-users of its quality. Many studies reference international standards like ISO and ASTM, which specify how materials should perform under various conditions.
Compliance with these standards is crucial not only for user safety but also for ensuring material reliability. It offers peace of mind, knowing that the material has undergone rigorous testing.
As such, decision-makers should look for findings from studies that align with recognized industry standards. This reinforces confidence in the reported efficacy of zirconium silicate compared to alternatives and supports informed procurement decisions.
- Standard Compliance Verification: Ensure the material meets relevant industry regulations.
- Quality Assurance Processes: Assess how adherence to standards impacts testing protocols.
- Impact on Product Lifecycle: Understand how standards can influence longevity and performance.
- Revising Standards as Industry Evolves: Keep abreast of changes in regulations that may affect material choice.
| Standard Organization | Key Focus | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO | Global quality standards | Assures reliability |
| ASTM | Testing protocols | Ensures performance |
What Insights Can Be Gained from Case Studies?
Case studies provide real-world insights that can guide material selection. They showcase how zirconium silicate performs in various industries and applications.
For instance, in dental applications, zirconium silicate has been used to create durable and aesthetic prosthetics. The resulting products not only withstand the rigors of daily use but also offer a pleasing appearance.
In the construction industry, case studies reveal that projects using zirconium silicate often report lower maintenance costs due to its durability. Projects that previously struggled with material failure were able to see significant improvements.
These practical examples can clarify how zirconium silicate might work for your specific needs and highlight successful implementations. By analyzing these insights, you’re better equipped to make evidence-based decisions.
- Industry-Specific Success Stories: Learn from others within your field who have successfully implemented zirconium silicate.
- Before-and-After Comparisons: Gauge how material changes impact performance and costs.
- Lessons Learned: Elevate your material choices by understanding past challenges others faced.
- Potential for Future Applications: Identify emerging trends and potential uses in your projects.
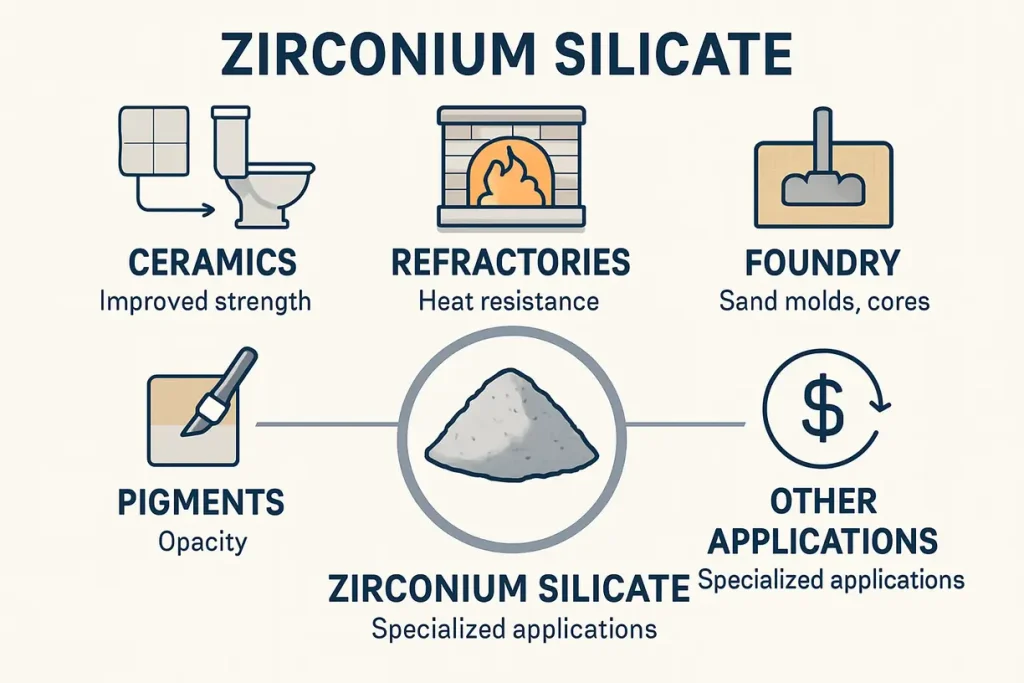
The image depicts visual examples of different industries benefiting from zirconium silicate.
How Does Zirconium Silicate Compare in Specific Applications?
In various applications, zirconium silicate proves its worth. Whether in dental work, manufacturing, or other fields, its effectiveness is well-documented.
In the dental industry, zirconium silicate is praised for its biocompatibility and ability to mimic the natural appearance of teeth. Dental professionals consistently choose it for crowns and bridges due to its strength and aesthetics.
In manufacturing, its thermal stability becomes a significant advantage. In high-temperature processes, zirconium silicate maintains its properties better than many alternatives, leading to better product quality and less downtime for equipment.
Identifying how zirconium silicate stacks up in specific applications allows decision-makers to find the best fit for their projects. Understanding its unique properties aids in making more informed material selections.
- Application-Specific Benefits: Explore unique advantages offered in each sector.
- Performance Metrics for Each Use: Different applications have different demands; document those metrics carefully.
- Stakeholder Testimonials: Gather feedback from those using zirconium silicate in real-world applications.
- Comparative Analysis with Alternatives: Regularly assess how zirconium silicate measures up against other options to validate choices.
| Application | Advantages | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Dental | Biocompatible, strong, aesthetic | Higher initial cost |
| Manufacturing | Thermal stability, durability | Limited knowledge on sourcing |
What Are the Potential Drawbacks of Zirconium Silicate?
While zirconium silicate has numerous advantages, it is essential to consider its potential drawbacks. Understanding these limitations allows for informed decision-making.
One notable concern is the initial cost. Zirconium silicate often comes at a higher upfront price compared to some alternatives, which can deter budget-conscious buyers. However, this cost should be weighed against its longevity and low maintenance needs.
Another drawback is the availability of supply. Depending on market conditions, sourcing zirconium silicate can sometimes be challenging. This aspect may affect project timelines if material is not readily accessible.
Potential risks also include its brittleness under certain conditions. While generally strong, zirconium silicate can crack if subjected to extreme impacts. Adequate handling and installation practices are crucial for minimizing this risk.
To address these concerns, consider the following:
- Budgeting for Upfront Costs: Factor material costs into the overall project budget.
- Exploring Supplier Options: Research multiple sources for more reliable procurement.
- Implementing Training for Installation: Ensure proper handling procedures to mitigate brittleness risks.
- Conducting a Material Risk Assessment: Identify and address potential failure points before project kick-off.
By being aware of these potential drawbacks, B2B buyers can take proactive measures to mitigate risks associated with zirconium silicate.
| Drawback | Impact | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Higher Initial Cost | Budget constraints | Long-term cost-benefit analysis |
| Availability | Supply chain issues | Establish reliable suppliers |
| Brittleness | Potential cracking in impact | Proper handling practices |
How Do Stakeholders Weigh the Benefits and Drawbacks?
In making material selections, stakeholders must carefully weigh the pros and cons of zirconium silicate. This process involves gathering comprehensive data and viewpoints from various departments.
For example, finance teams may focus on cost implications, while production teams might emphasize material performance and reliability. Balancing these perspectives ensures that decisions align with both financial goals and operational needs.
Frequently, organizations conduct internal reviews to assess the material’s fit. This includes comparing alternatives, evaluating overall project impact, and engaging in discussions across teams.
Ultimately, the goal is to achieve consensus on material selection by reinforcing the benefits over the drawbacks. Engaging all stakeholders fosters a sense of ownership in the decision-making process, leading to better project outcomes.
- Interdepartmental Collaboration: Facilitate discussions to gather diverse insights into material performance.
- Shared Decision Framework: Utilize a structured approach for evaluating options based on company priorities.
- Continuous Feedback Mechanisms: Establish processes for gathering ongoing input as projects progress.
- Documentation of Previous Decisions: Track how previous selections performed to inform future choices.
| Stakeholder Group | Concern | Contribution |
|---|---|---|
| Finance | Cost implications | Budget assessments |
| Production | Material performance | Operational reliability |
| Management | Project impact | Strategic decision-making |
What Future Trends Are Emerging in Material Comparisons?
Future trends indicate significant changes in how materials are evaluated. Emerging technologies offer new ways to compare and assess the efficacy of materials like zirconium silicate.
For example, advancements in testing methods may provide more precise data on material behavior under various conditions. Simulation technologies allow for better predictions of performance, making evaluations quicker and more efficient.
Sustainability is another vital trend shaping material choices. Companies are increasingly seeking environmentally friendly options, leading to adaptations in material formulations.
As these trends continue to develop, keeping an eye on how they influence material comparisons is essential. Staying ahead of these changes ensures your organization is poised to adopt the best solutions available.
- Enhanced Analytical Tools: Look for new software or methodologies that improve material analysis.
- Sustainable Material Innovations: Monitor shifts toward greener materials and production processes.
- Digital Twin Technologies: Utilize virtual simulations to predict material performance without physical tests.
- Greater Focus on Lifecycle Impact: Assess entire lifecycles rather than just initial performance metrics.
Why Is Understanding Efficacy Critical for B2B Buyers?
For B2B buyers, grasping the efficacy of materials is pivotal to making sound purchasing decisions. The choice of material can significantly influence both the short-term and long-term success of a project. When materials perform optimally, they not only enhance the overall product effectiveness but also contribute to significant cost reductions over time.
Understanding how zirconium silicate compares to its alternatives allows buyers to assess potential impacts on project timelines, quality, and operational efficiency. Knowledge of material characteristics, such as durability and maintenance needs, informs choices that lead to successful project outcomes and satisfied stakeholders.
Moreover, investing time in understanding these materials can create substantial long-term gains for organizations. Buyers who are well-versed in the benefits and limitations of zirconium silicate are better positioned to negotiate favorable terms and secure quality products that align with their business goals.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the efficacy of zirconium silicate through comprehensive comparative studies is essential for making informed material selections in various industries. The detailed analysis of its advantages, performance metrics, cost-effectiveness, and compliance with industry standards provides a clear picture of its capabilities. While there are alternative materials available, zirconium silicate consistently demonstrates superior performance, particularly in applications demanding durability and aesthetic appeal.
Moreover, assessing the potential drawbacks and engaging stakeholders in the decision-making process ensures a balanced approach. By anticipating future trends and staying informed about innovations, organizations can enhance project outcomes and achieve long-term success. Ultimately, the informed selection of zirconium silicate or its alternatives can significantly impact operational efficiency and profitability.
FAQ Section
Q1: What makes zirconium silicate a preferred option?
Zirconium silicate is highly regarded for its exceptional properties, including high durability, chemical inertness, and excellent aesthetic qualities. These attributes make it a favored choice in industries such as dental prosthetics and manufacturing, where both performance and appearance matter significantly.
Q2: How are comparative studies relevant for material selection?
Comparative studies are crucial as they provide systematic evaluations of different materials based on performance metrics, cost implications, and suitability for specific applications. By analyzing empirical data from these studies, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that align with industry standards and project requirements.
Q3: What industries benefit most from zirconium silicate?
Industries such as dental, aerospace, and ceramics particularly benefit from zirconium silicate. In dental applications, for example, its biocompatibility and resilience make it ideal for crowns and bridges. In aerospace, its thermal stability ensures reliable performance in extreme conditions.
Q4: Are there any risks associated with using zirconium silicate?
While zirconium silicate is generally reliable, some potential risks include its higher initial costs compared to alternatives and its brittleness under specific circumstances. Proper handling and installation practices are essential to mitigate these risks and ensure optimal performance over time.
Q5: How can organizations stay updated on material innovations?
Organizations can remain informed about material innovations by subscribing to industry journals, attending conferences, and collaborating with material suppliers. Additionally, engaging in professional networks and following advancements in materials science can provide insights into emerging trends and technologies.