Finding a material that offers exceptional durability, heat resistance, and a flawless finish for your industrial products can be a constant struggle. You need a solution that doesn’t compromise on quality or performance. Inferior materials lead to product failures, increased production costs, and a damaged reputation, putting you at a competitive disadvantage. Zirconium Silicate is the versatile, high-performance compound that directly addresses these challenges, and this guide shows you how its unique properties can elevate your products.
Key Properties of Zirconium Silicate
What makes it so durable?
Its durability comes from its incredibly hard and stable crystalline structure. Here’s the deal: it delivers top-tier resistance to physical wear and chemical attacks.
- Hardness: Resists scratches and surface damage.
- Abrasion Resistance: Withstands friction and grinding forces.
- Chemical Stability: Remains inert when exposed to acids and alkalis.
How does it perform under extreme heat?
It performs exceptionally well under extreme heat due to its high melting point and low thermal expansion. This means it maintains its structural integrity without warping or cracking when temperatures soar.
Why is its stability so important?
Its stability guarantees consistent, reliable performance in the most demanding industrial environments. This ensures your products last longer and maintain their quality over time. Key Takeaway: The combination of hardness, heat resistance, and stability makes it a go-to material for high-stress applications.
| Property | Zirconium Silicate | Alumina (Alternative) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness (Mohs) | 7.5 | 9.0 | |
| Melting Point | ~2,550°C (4,622°F) | ~2,072°C (3,762°F) | |
| Thermal Expansion | Low | Moderate |
Zirconium Silicate in the Ceramics Industry

How does it create a perfect glaze?
It creates a perfect glaze by providing a smooth, hard, and chemically resistant surface. The secret is its fine particle size, which allows for a flawless, uniform coating when fired.
Why is it a superior opacifier?
It is a superior opacifier because its high refractive index effectively scatters light to create a brilliant, pure white finish. Think of it this way:
- Brilliant Opacity: Achieves bright white with less material.
- Color Stability: Ensures true, stable colors in pigmented glazes.
- Uniformity: Provides a consistent, non-blotchy appearance.
Can it improve ceramic tile appearance?
Yes, it significantly improves tile appearance by enhancing whiteness, brightness, and overall durability. This allows you to produce high-quality tiles that resist both scratches and stains. Key Takeaway: Zirconium silicate is essential for achieving the bright, white, and durable finish that defines high-quality ceramics. You can learn more about improving glaze smoothness in our blog.
| Role in Ceramics | Primary Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Glaze Component | Provides a hard, smooth, and chemically resistant surface. | |
| Opacifier | Delivers brilliant whiteness and opacity. | |
| Pigment Stabilizer | Ensures vibrant and consistent color expression. |
Using Zirconium Silicate for Refractories

What are refractory applications?
Refractory applications involve materials used to line high-temperature furnaces, kilns, and reactors. Here’s the bottom line: they must withstand extreme heat and chemical corrosion to function properly.
How does it protect kiln furniture?
It protects kiln furniture by forming a non-reactive barrier that resists thermal shock and prevents materials from sticking. This translates directly to:
- Longevity: Extends the usable life of kiln shelves and supports.
- Thermal Shock Resistance: Prevents cracking during rapid heating and cooling.
- Structural Integrity: Maintains strength at high temperatures.
Why is it used for crucibles?
It is used for crucibles because of its excellent thermal stability and resistance to corrosion from molten metals. This ensures the crucible won’t break down or contaminate the melt. Key Takeaway: Its ability to withstand extreme heat and chemical attack makes it indispensable for extending the life of refractory components.You can learn more about preventing cracks in ceramics in our blog.
| Refractory Item | How Zirconium Silicate Enhances It | |
|---|---|---|
| Kiln Furniture | Provides a protective coating that resists sticking and thermal shock. | |
| Crucibles | Offers high strength and resistance to molten metal corrosion. | |
| Refractory Coatings | Creates a durable, non-porous barrier against heat and chemicals. |
Zirconium Silicate in Foundry Casting
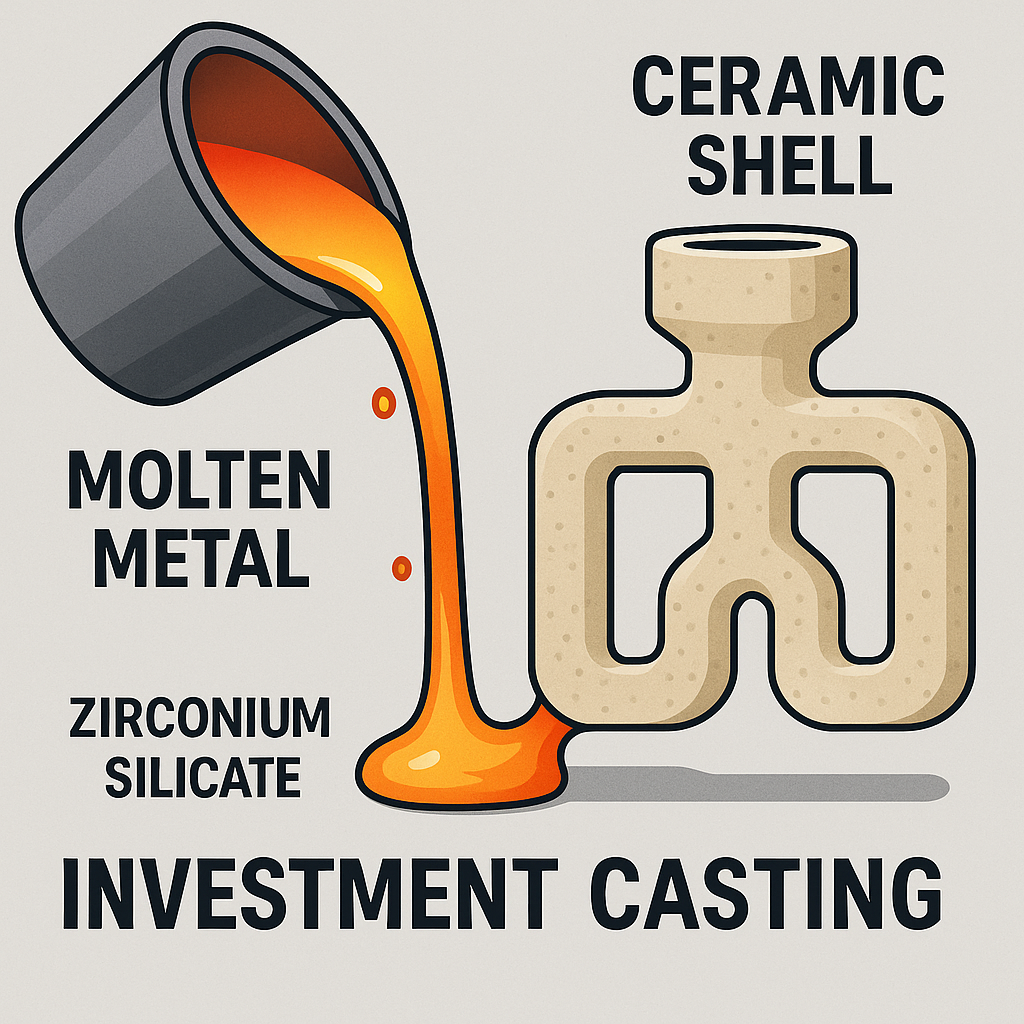
How does it strengthen casting molds?
It strengthens casting molds by providing high thermal stability and resistance to molten metal. Look at the benefits this delivers for you:
- Reduced Cracking: Minimizes mold failure during casting.
- Improved Mold Strength: Ensures molds hold their precise shape.
- Better Surface Finish: Creates a smoother initial cast part.
What is its role in investment casting?
Its primary role in investment casting is to form the crucial face coat of the ceramic shell. The reason is simple: it captures intricate details from the wax pattern with perfect fidelity.
Can it improve casting surface finish?
Absolutely, it dramatically improves the surface finish of castings by creating a very smooth, non-reactive mold surface. This reduces the need for extensive and costly post-processing work. Key Takeaway: Using zirconium silicate in foundry molds is the key to achieving high-precision castings with superior surface quality.
| Foundry Molds | Without Zirconium Silicate | With Zirconium Silicate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Quality | Rougher finish, potential for metal penetration. | Smooth, clean finish with high fidelity. | |
| Defect Rate | Higher risk of cracking and thermal-related defects. | Lower defect rate due to high thermal stability. | |
| Post-Processing | Requires more grinding and finishing. | Minimal finishing required, saving time and labor. |
The Power of Zirconium Silicate in Dentistry
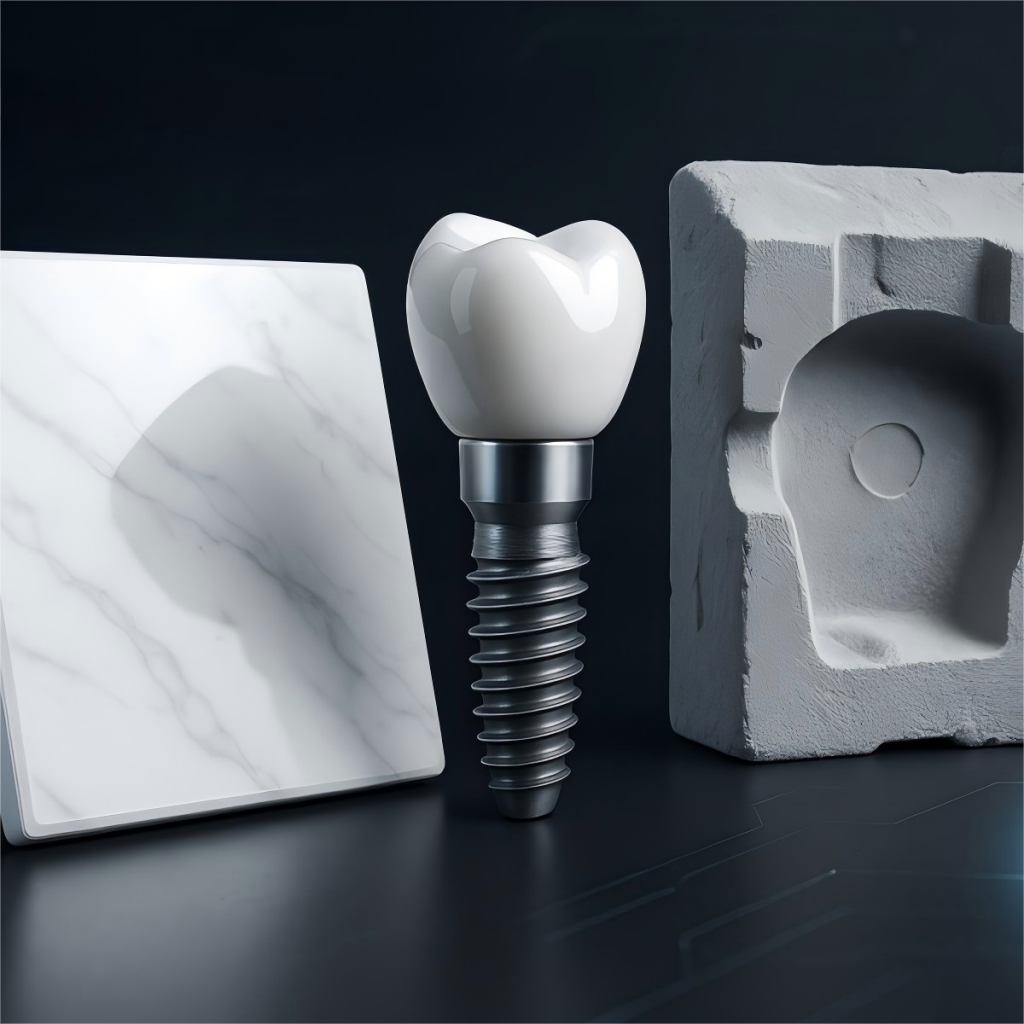

Why is biocompatibility so crucial?
Biocompatibility is crucial because any material placed in the body must not cause a toxic or allergic reaction. You need a material that is safe and integrates well with human tissue.
How are dental crowns made with it?
Dental crowns and bridges are often made from milled zirconia, which is derived from zirconium silicate. This process ensures exceptional:
- Strength: Creates restorations that can withstand biting forces.
- Aesthetic Properties: Mimics the translucency and color of natural teeth.
- Longevity: Provides a durable, long-lasting dental solution.
What makes it ideal for restorations?
Its combination of superior strength, excellent aesthetics, and proven biocompatibility makes it an ideal material for modern dental restorations. Put simply, it delivers both function and beauty. Key Takeaway: Zirconium silicate derivatives offer the strength and biocompatibility needed for safe, durable, and natural-looking dental work.
| Feature | Zirconium Silicate (Zirconia) | Traditional Dental Materials (e.g., PFM) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Strength | Very High | Moderate to High | |
| Aesthetics | Excellent (tooth-colored) | Good (metal base can show) | |
| Biocompatibility | Excellent | Good (potential for metal allergies) |
Zirconium Silicate as a Superior Abrasive

What makes it effective for grinding?
Its high hardness and uniform particle shape make it extremely effective for precision grinding and milling. But there’s more to it: its high density provides greater impact energy.
Where is it used as a grinding media?
It is widely used as a grinding media in various industrial processes that require fine, contamination-free results. Common applications include:
- Ball Mills: For grinding pigments, minerals, and ceramics.
- Sand Mills: For dispersing and milling inks and coatings.
- Polishing Processes: For achieving a smooth finish on metals and glass.
Can you use it for fine polishing?
Yes, you can use it for fine polishing applications where a smooth, high-gloss surface is required. Its fine, hard particles gently remove microscopic imperfections without scratching the material. Key Takeaway: The hardness and density of zirconium silicate beads make them an efficient and low-contamination choice for industrial grinding and polishing.
| Abrasive Application | Key Property Utilized | |
|---|---|---|
| Grinding & Milling | High Density & Hardness | |
| Polishing | Fine Particle Size & Hardness | |
| Sandblasting | Hardness & Abrasion Resistance |
Decorative Uses of Zirconium Silicate. You can learn more about zirconium silicate color variation in our blog.
Decorative Uses of Zirconium Silicate
How does it enhance glass opacity?
It enhances glass opacity by acting as a powerful opacifier, creating a uniform, milky-white appearance. The secret is its ability to form fine, light-scattering crystals within the glass matrix.
What effects does it create in tiles?
In tiles, it is the key ingredient for achieving a bright, opaque base glaze. This allows you to create products with:
- Improved Gloss: Provides a smooth, reflective surface.
- Enhanced Color Vibrancy: Makes decorative colors pop.
- Unique Textures: Can be used to create matt or satin finishes.
Can it achieve different visual effects?
Yes, by varying the particle size and concentration, you can achieve a range of visual effects from a deep, opaque white to a soft, translucent finish in glazes and glass. Key Takeaway: Zirconium silicate is a versatile tool for controlling opacity, brightness, and color, making it invaluable in decorative applications.
| Decorative Effect | Industry Beneficiary | |
|---|---|---|
| Opacity & Whiteness | Glass, Ceramics, Tile | |
| Gloss & Smoothness | Tile, Sanitaryware | |
| Color Vibrancy | Artistic Pottery, Decorative Glass |
Zirconium Silicate for Protective Coatings

What materials need protective coatings?
Metals, alloys, and even other ceramics often require protective coatings in harsh industrial settings. The bottom line is that these coatings shield them from high temperatures, chemicals, and physical wear.
How does it resist corrosion and erosion?
It resists damage by forming a dense, non-porous, and chemically inert barrier on the surface of a material. This single layer provides robust protection against multiple threats:
- Heat: Acts as a thermal barrier in high-temperature zones.
- Chemical Corrosion: Shields against acids, alkalis, and molten metals.
- Physical Erosion: Resists wear from abrasive particles.
How does this prolong equipment lifespan?
This protection directly prolongs equipment lifespan by preventing the degradation of critical components. It reduces downtime, lowers maintenance costs, and improves operational reliability for you. Key Takeaway: Zirconium silicate-based coatings provide a multi-functional shield that significantly extends the service life of industrial equipment.
| Type of Protection | Resulting Benefit | |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Barrier | Prevents heat damage, maintains component strength. | |
| Chemical Resistance | Stops corrosive attacks, prevents contamination. | |
| Physical Hardness | Reduces wear and tear from erosion and abrasion. |
How to Handle Zirconium Silicate Safely

What are the main safety risks?
The main safety risk associated with zirconium silicate is the inhalation of fine dust particles. You must avoid breathing in the powder, as prolonged exposure can lead to respiratory issues.
What equipment is needed for dust control?
Proper equipment is essential to minimize dust exposure and ensure a safe working environment. Be sure to use:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): NIOSH-approved respirators, safety goggles, and gloves are mandatory.
- Ventilation: Use local exhaust ventilation systems to capture dust at the source.
Are there disposal regulations to follow?
Yes, you should always handle disposal according to local, state, and federal regulations. While not typically classified as hazardous waste, it’s best to confirm the proper procedures. Key Takeaway: Safe handling hinges on effective dust control through proper ventilation and the consistent use of personal protective equipment.
| Safety Step | Action Item | |
|---|---|---|
| Handling | Wear appropriate PPE (respirator, gloves, goggles). | |
| Storage | Keep in a cool, dry place in sealed containers. | |
| Disposal | Follow all local, state, and federal guidelines. |
The Future of Zirconium Silicate Uses
What new research is being done?
New research is focused on creating nanostructured zirconium silicate and composites with enhanced properties. The goal is to unlock even greater performance in thermal, mechanical, and optical applications.
Could it be used in electronics/aerospace?
Yes, its potential in these advanced sectors is significant and growing. Researchers are exploring its use in:
- Advanced Composites: For lightweight, high-strength components.
- Thermal Barriers: For next-generation jet engine turbine coatings.
- Specialty Electronics: As a dielectric material in capacitors and insulators.
How will its role in manufacturing evolve?
Its role will evolve from being a trusted additive to an enabling material for breakthrough technologies. As purity and material science improve, you can expect it to solve next-generation challenges. Key Takeaway: Ongoing research is set to expand zirconium silicate’s use into cutting-edge aerospace, electronics, and advanced materials sectors.
| Current Industry | Potential Future Industry | |
|---|---|---|
| Ceramics & Refractories | Advanced Composites & 3D Printing | |
| Foundry & Casting | Aerospace Turbine Components | |
| Dental Materials | Biomedical Implants & Scaffolds |
Elevate Your Standards with Zirconium Silicate
Zirconium Silicate provides a reliable, high-performance solution for durability, heat resistance, and aesthetic quality. We are committed to providing innovative materials that empower you to lead your industry and create superior products. Ready to see how high-performance Zirconium Silicate can transform your production process? Contact our materials experts today for a personalized consultation and sourcing information.
Your Zirconium Silicate Questions Answered
Q1:Can I use Zirconium Silicate for food-grade ceramic glazes?Yes, absolutely. When properly formulated and fired, zirconium silicate is an inert and stable component, making it safe and widely used for food-contact ceramic glazes.
Q2:What’s the best way to ensure uniform mixing in a glaze?The best way is to use high-shear mixing or ball milling. This breaks down any agglomerates and ensures the fine zirconium silicate particles are evenly dispersed throughout the glaze slurry.
Q3:Is Zirconium Silicate the same thing as Zirconia?No, they are different but related. Zirconium Silicate (ZrSiO₄) is a naturally occurring mineral, while Zirconia (ZrO₂) is Zirconium Oxide, a highly processed ceramic often produced from zirconium silicate.
Q4:How does Zirconium Silicate compare to tin oxide as an opacifier?It is a more cost-effective and often more efficient opacifier. While both produce excellent whiteness, zirconium silicate typically provides comparable or better opacity at a lower price point.
Q5:Can I safely handle small quantities for a home pottery studio?Yes, with proper precautions. Always wear a dust mask or respirator, work in a well-ventilated area, and use wet cleanup methods to avoid creating airborne dust.