ZrSiO₄
Zirconium Silicate
Request free samples or customize your ZrSiO₄ solution.
ZrSiO₄
Zirconium Silicate
Zirconium silicate (ZrSiO₄) is a versatile material primarily derived from natural zircon sand, widely applied in industrial fields. It mainly exists in two forms: zirconium silicate powder, used in ceramic glazes and refractory materials, and zirconium silicate beads, serving as efficient grinding media. With its excellent physicochemical properties, zirconium silicate plays a crucial role in numerous industries including ceramics, coatings, casting, and electronic materials.

ZrSiO₄
Zirconium Silicate Powder
Zirconium silicate powder is a high-performance inorganic material derived from natural zircon sand through high-temperature calcination, precision grinding, and classification processes. Combining excellent chemical stability, high-temperature resistance (melting point >2500°C), and high refractive index, it serves as a versatile material widely adopted across industrial applications.
Key Features
- Ultra-High Purity: ZrSiO₄ content ≥98.5%, with heavy metal impurities (Fe, Ti, etc.) <0.1%, meeting electronic-grade requirements.
- Corrosion Resistance: Stable in harsh environments, including strong acids (sulfuric, hydrochloric), alkalis, and molten salts.
- Precise Particle Size: Adjustable D50 particle size: 0.5–20μm, compatible with dry/wet dispersion for spraying, injection molding, etc.
- Eco-Safe: Non-radioactive, compliant with RoHS and REACH standards, suitable for food-contact applications.
Advantages
- Cost-Effective Performance: 35–50% cost reduction compared to zirconia powder, ideal for large-scale industrial use.
- Process Compatibility: Custom surface treatments (e.g., silane coating) to optimize bonding with resin/metal matrices.
- Global Supply: Samples (from 1kg) to bulk orders (100+ tons), backed by technical reports and application guidance.

| Zirconium Silicate Powder Physicochemical Index |
|---|
| Formula | Properties | Packing |
|---|---|---|
| ZrSiO₄ | Offwhite powder, high chemical stability | Composite paper bags in 40 kgs |
| Product | ZrO₂ | D50(um) | D90(um) | Fe₂O₃ | TiO₂ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 65 Zirconium | ≥65% | 0.950 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.10 | <0.15 |
| 64 Zirconium | ≥64% | 0.978 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.10 | <0.15 |
| 60 Zirconium | ≥60% | 0.913 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.15 | <0.15 |
| 55 Zirconium | ≥55% | 0.900 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.20 | <0.15 |
| 46 Zirconium | ≥46% | 0.900 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.20 | <0.15 |
| 40 Zirconium | ≥40% | 0.900 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.20 | <0.15 |
| 33 Zirconium | ≥33% | 0.900 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.20 | <0.15 |
| 25 Zirconium (embryo) | ≥25% | 1.200 | 1.6-1.7 | <0.30 | <0.15 |
Note: Specifcafions can be customized to customer’srequirements
Where does Zirconium Silicate Powder originate? How is high-purity zirconium silicate extracted from natural minerals?
Zirconium silicate (ZrSiO4) is an important non-metallic mineral, and its main raw material is natural zircon sand. Zircon sand is an abundant zirconium-element mineral on Earth, primarily found in coastal sand mines and alluvial deposits. Major global zircon sand producing areas include Australia, South Africa, the United States, Indonesia, and China. These zircon sand deposits are often associated with heavy minerals such as ilmenite and rutile.

1.1 Formation and Characteristics of Zircon Sand
1.2 Extraction and Purification of Zirconium Silicate Powder
- Gravity Separation and Magnetic Separation: Utilizing differences in density and magnetism between zircon sand and associated minerals for separation, initially removing most impurities.
- Flotation: By adding flotation agents, zircon sand or impurity minerals are selectively floated to the surface of the water, further improving purity.
- Acid and Alkali Leaching: Using acid or alkali solutions to dissolve iron, titanium, and other oxide impurities on the surface of zircon sand for deep purification. For example, sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid can effectively remove iron impurities, while sodium hydroxide solution can be used to remove silicate impurities.
- High-Temperature Chlorination: This is a more advanced purification method, where impurities are converted into volatile chlorides by reacting with chlorine gas at high temperatures, thereby achieving the preparation of high-purity zirconium silicate. This method can yield higher purity products but at a higher cost.
After multiple purification processes, the purity of zircon sand can reach over 99%, laying the foundation for the subsequent production of high-quality zirconium silicate powder. The purified zircon sand then undergoes ultra-fine grinding, classification, and other physical processing to obtain zirconium silicate powder with different particle size distributions.
How is Zirconium Silicate Powder produced? What are the differences between dry and wet processes?
2.1 Dry Production Process
2.2 Wet Production Process
2.3 Surface Modification Technology
3. What types of Zirconium Silicate Powder are there? How to choose the most suitable product based on purity, particle size, morphology, and modification?
3.1 Classification by Purity
3.2 Classification by Particle Size
3.3 Classification by Morphology
3.4 Classification by Surface Modification
4. Why is Zirconium Silicate Powder so unique? What key physical and chemical properties does it possess?
4.1 Crystal Structure and Stability
4.2 Thermal Properties
4.3 Mechanical Properties
4.4 Chemical Properties
4.5 Optical Properties
Application of Zirconium Silicate Powder
Zirconium silicate powder, with its excellent physicochemical properties, plays a crucial role in numerous industrial fields, and its application prospects are continuously expanding with the ongoing development of new technologies.
With the advancement of industrial technology and increasing demands for material performance, the application areas of zirconium silicate powder will continue to expand, especially in high-performance ceramics, environmentally friendly materials, and new energy fields, where market demand will continue to grow.

Ceramic Industry
- Ceramic Glazes: Zirconium silicate powder is the most important opacifier and whitening agent in ceramic glazes. Due to its high refractive index and good chemical stability, it can impart excellent whiteness, gloss, and opacity to the glaze surface, while also improving the hardness and wear resistance of the glaze. Zirconium silicate powders of different particle sizes can be used to produce matte, semi-matte, or glossy glazes.
- Ceramic Bodies: In certain special ceramic bodies, zirconium silicate powder can also be used as an additive to improve the sintering performance, mechanical strength, and thermal shock stability of the body.

Refractory Materials
- Refractory Bricks and Castables: Used in the production of refractory bricks and castables for high-temperature equipment such as glass melting furnaces, steel industrial furnace linings, and non-ferrous metal smelting furnaces, significantly extending the service life of furnace linings and improving corrosion resistance.
- High-Temperature Coatings: As a component of high-temperature coatings, used to protect metal or ceramic surfaces from high-temperature oxidation and corrosion.
Foundry Industry
- Foundry Coatings: Zirconium silicate foundry coatings have excellent refractoriness, low thermal expansion, and good suspension properties, effectively preventing metal penetration and improving the surface finish of castings, especially suitable for high-temperature alloy castings such as cast steel and cast iron.
- Special Molding Sand: In precision casting, zirconium silicate sand can be used as a special molding sand due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and good thermal conductivity, ensuring the dimensional accuracy and surface quality of castings.

Paints and Inks
- White Pigment and Filler: As an efficient white pigment and filler, it can improve the hiding power, whiteness, and weather resistance of paints and inks.
- Functional Coatings: In certain functional coatings, such as wear-resistant coatings and anti-corrosion coatings, zirconium silicate powder can be used as an enhancing component to improve the hardness and durability of the coating.

Other Emerging Applications
- Nuclear Industry: Due to its small neutron absorption cross-section, zirconium silicate can be used as fuel cladding material or structural material in nuclear reactors.
- Biomedical Materials: In the field of bioceramics and biocompatible coatings, zirconium silicate has good biocompatibility and can be used to manufacture dental materials, bone repair materials, etc.
- Catalyst Carriers: As an inert carrier, it can be used to load active components and play a role in certain catalytic reactions.

Ask for a quotation
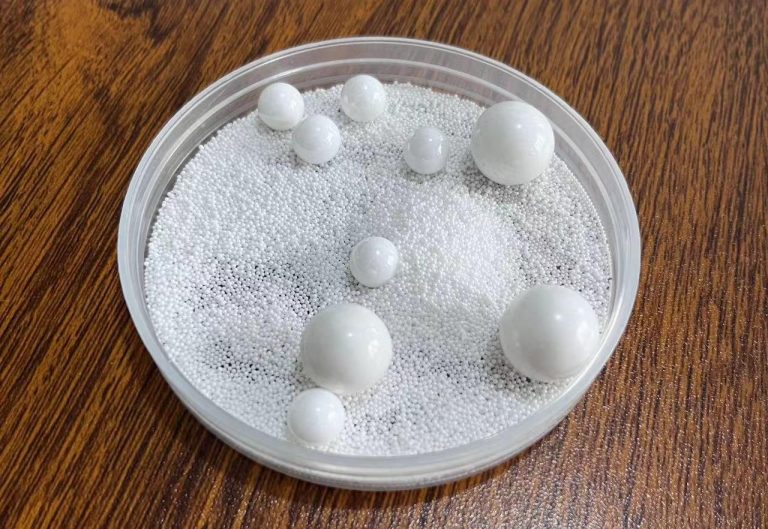
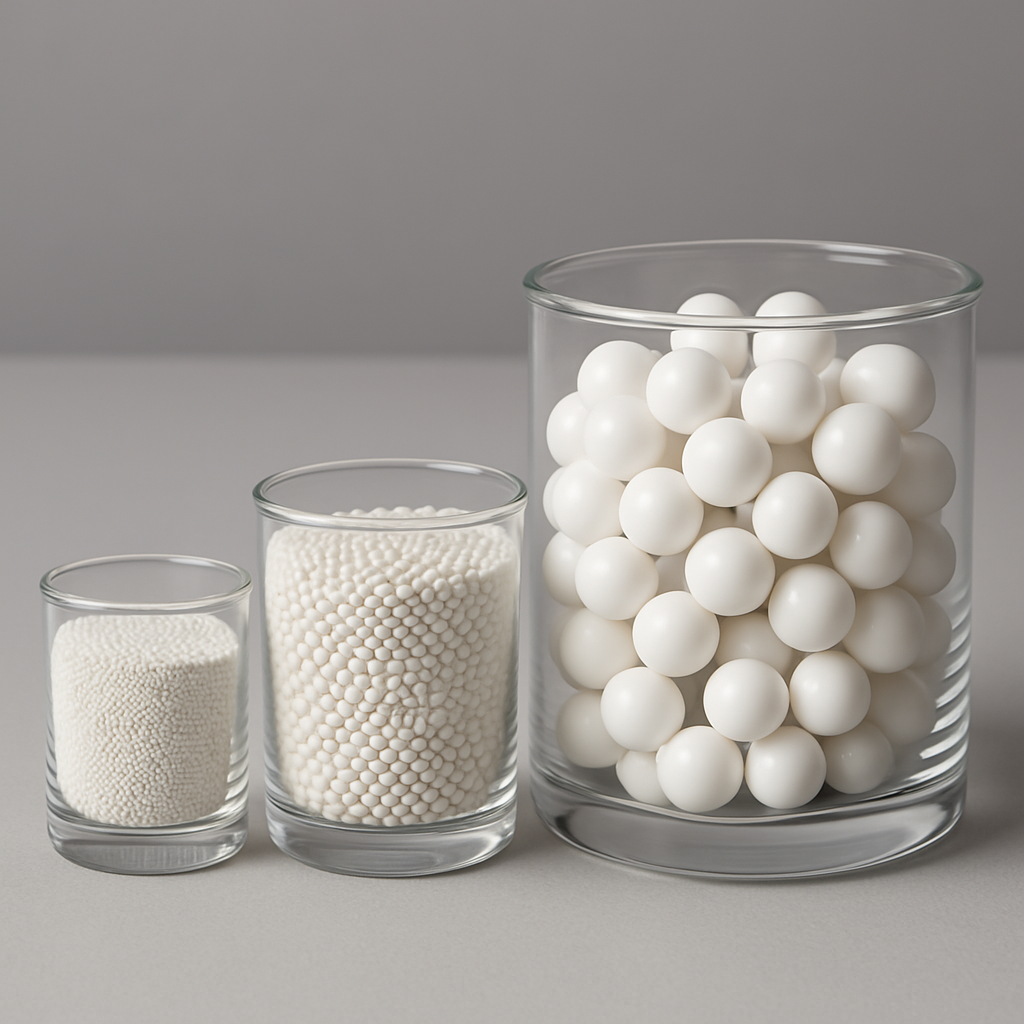
ZrSiO₄ Beads
Zirconium Silicate Beads (ZrSiO₄ Beads)
Zirconium silicate beads (chemical formula ZrSiO₄) are high-performance ceramic grinding media known for their cost-effectiveness, moderate hardness (Mohs hardness ~7.5), and excellent chemical stability. Produced from natural zircon sand via high-temperature sintering, they exhibit low metal ion leaching, making them ideal for cost-sensitive grinding applications with moderate contamination tolerance.
Key Features:
- Cost-Effective: Significantly lower cost compared to zirconia beads, suitable for large-scale industrial grinding (e.g., ceramic glazes, mineral fillers).
- Acid/Alkali Resistance: Stable in pH 3-11 environments, compatible with water-based and some solvent-based systems.
- Uniform Particle Size Distribution: Available in 0.5mm to 5mm sizes, compatible with sand mills, agitator mills, and other equipment, ensuring consistent grinding efficiency.
| Product Specification |
|---|
| Chemical Composition |
| ZrO₂ | SiO₂ | Others |
|---|---|---|
| ≥65% | 30-35% | ≤1.00% |
Note: Chemical composition depends on specfications
| Physical Charactenstics |
|---|
| Densily | Bulk Density | Vickers Hardness |
|---|---|---|
| >4.1g/cm³ | ≥2.5g/cm³ | >900Hv |
| Specifications(mm) |
|---|
| Ф0.6-0.8 | Ф0.8-1.0 | Ф1.0-1.2 | Ф1.2-1.4 | Ф1.4-1.6 |
| Ф1.6-1.8 | Ф1.8-2.0 | Ф2.5-3.0 | Ф3.0-3.5 | Ф4 |
| Ф5 | Ф6 | Ф7 | Ф8 | Ф10 |
Note: Specificafions can be customized to customer’s requirements.
What are the raw material sources and basic composition of Zirconium Silicate Beads?

What are the production processes and forming technologies for Zirconium Silicate Beads?
What are the product types and specifications of Zirconium Silicate Beads?

What key physical and chemical properties do Zirconium Silicate Beads possess?
1. High Density: With a typical density of 3.8-4.1 g/cm³, zirconium silicate beads provide sufficient kinetic energy for efficient grinding and dispersion of various materials.

What are the application areas and selection guidelines for Zirconium Silicate Beads?
Zirconium silicate beads are widely used across various industries due to their superior grinding and dispersion capabilities. Their selection depends on the specific application requirements, including the material to be milled, desired fineness, and type of grinding equipment.

Coatings and Ink Industry
In the coatings and inks industry, zirconium silicate beads are extensively used for grinding and dispersing pigments, dyes, and fillers. They are particularly effective in producing high-quality paints, automotive coatings, printing inks, and digital inkjet inks, where fine particle size and uniform dispersion are critical for color strength, gloss, and stability.

Electronic Materials Industry
The electronic materials industry utilizes zirconium silicate beads for the ultra-fine grinding and dispersion of ceramic powders, conductive pastes, and dielectric materials. Applications include the manufacturing of multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), ceramic substrates, and various electronic components, where precise particle size control and high purity are paramount.

Fine Chemical Industry
Zirconium silicate beads find applications in the fine chemical industry for grinding and dispersing a wide range of chemical products, including pesticides, agrochemicals, pharmaceutical intermediates, and specialty chemicals. Their chemical inertness ensures that the beads do not contaminate the sensitive chemical formulations.

Ceramics and Mineral Processing Industry
In the ceramics and mineral processing industry, these beads are used for grinding raw materials such as kaolin, calcium carbonate, and other mineral fillers to achieve desired particle sizes for ceramic bodies, glazes, and other mineral-based products. Their durability makes them suitable for heavy-duty grinding operations.

Metal Surface Treatment Industry
Zirconium silicate beads are also employed in the metal surface treatment industry for shot peening, deburring, and surface finishing of metal parts. Their hardness and spherical shape provide a consistent and effective means of improving surface properties, reducing fatigue, and enhancing the aesthetic appeal of metal components.
How to select Zirconium Silicate Beads?

Precision-Engineered Zirconium Silicate: Purity You Can Trust
At Global Industry, we understand that in the demanding world of industrial manufacturing, the purity of raw materials is not just a preference—it's a critical requirement. Our Zirconium Silicate is meticulously processed to achieve an unrivaled level of purity, ensuring consistent performance and superior end-product quality for our B2B partners. We leverage advanced beneficiation techniques and stringent quality control protocols throughout our production cycle, from raw ore sourcing to final product packaging. This commitment to purity directly translates into enhanced material properties for your applications, reducing defects, optimizing processes, and ultimately safeguarding your investment. Whether for advanced ceramics, precision casting, or specialized refractories, our Zirconium Silicate provides the foundational integrity your operations demand, minimizing impurities that could compromise performance and maximizing the efficiency of your production lines. Choose Global Industry for Zirconium Silicate that sets the benchmark for industrial purity and reliability.

Advanced Manufacturing Capabilities: Your Strategic Supply Partner
As a leading factory in China, Global Industry boasts state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities specifically designed for the high-volume production of Zirconium Silicate. Our advanced production lines incorporate cutting-edge technology and automated processes, guaranteeing not only consistent product quality but also the capacity to meet the most demanding supply requirements of our global B2B clientele. We understand the critical importance of a reliable supply chain in maintaining your production schedules and minimizing downtime. Our robust infrastructure, coupled with efficient logistics and a dedicated team, ensures timely delivery and seamless integration into your operations. By partnering with Global Industry, you gain a strategic supplier capable of providing the scale, consistency, and reliability essential for your long-term success. Our commitment to continuous improvement in manufacturing processes means you benefit from the latest advancements in material production, ensuring a competitive edge in your respective markets.
Tailored Solutions and Technical Expertise: Beyond Just a Supplier
At Global Industry, we believe in fostering true partnerships with our clients, extending beyond mere transactional relationships. Our team of experienced material scientists and technical experts is dedicated to providing tailored solutions and comprehensive support for your specific application needs. We understand that each industry and even each client may have unique requirements for Zirconium Silicate. Whether you need specific particle size distributions, customized chemical compositions, or advice on optimizing material integration into your processes, our technical team is ready to collaborate. We offer in-depth technical consultations, material analysis, and R&D support to help you achieve optimal performance and overcome complex challenges. This commitment to collaborative innovation ensures that you not only receive a high-quality product but also gain a valuable resource in material science, helping you drive efficiency, reduce costs, and develop cutting-edge products.

Global Reach and Reliable Logistics: Your Seamless Supply Chain Solution
With Global Industry, geographical distance is no barrier to accessing premium Zirconium Silicate. As a factory based in China, we have established a robust global logistics network and extensive experience in international trade, ensuring efficient and reliable delivery of our products to clients worldwide. We manage the complexities of export documentation, customs procedures, and international shipping, providing a seamless supply chain solution from our factory floor directly to your production facility. Our commitment to timely and secure delivery minimizes your logistical concerns and allows you to focus on your core business. We offer flexible packaging and shipping options to accommodate diverse client needs, ensuring that your Zirconium Silicate arrives in optimal condition, ready for immediate use. Partner with Global Industry for a truly global reach and a supply chain solution that prioritizes your operational continuity and peace of mind.
FAQ
Ask for A Free Quote

