Zirconia powder is essential in various industries due to its properties, including strength and thermal resistance. However, ensuring its quality according to international standards can be a challenge. Many businesses face concerns about the reliability of their zirconia powder suppliers and the testing methods used to verify quality. Fortunately, this article provides in-depth insights into the testing procedures that ensure zirconia powder meets rigorous standards. By understanding these methods, purchasing managers can make informed decisions that enhance product quality and compliance, ultimately leading to better operational outcomes.
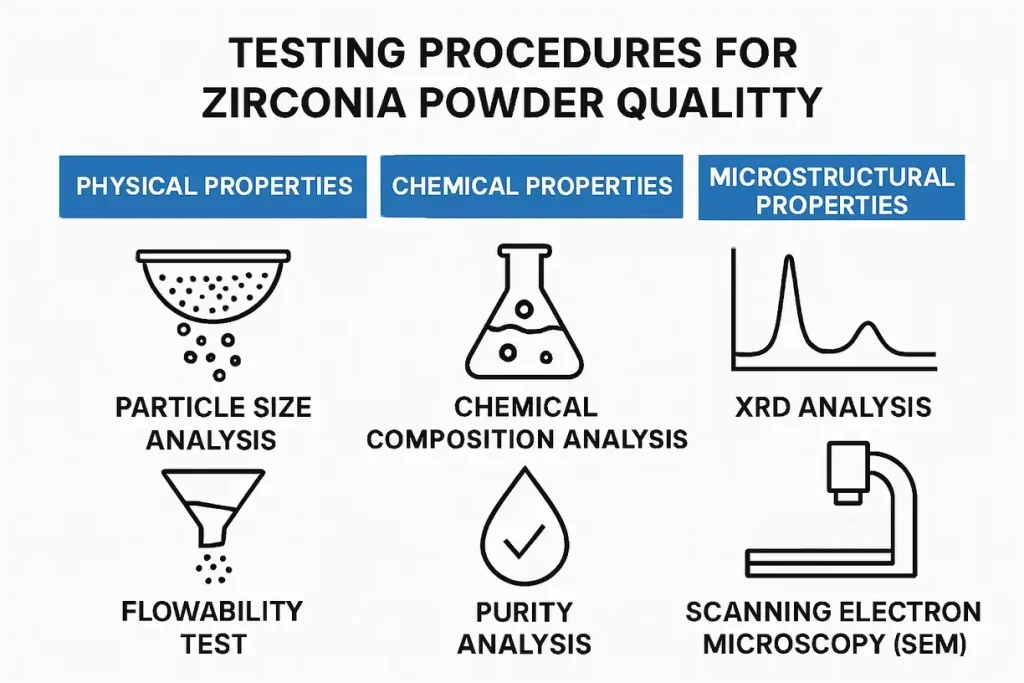
This image illustrates various testing procedures for assessing zirconia powder quality.
What Are the Specific Standards for Zirconia Powder Quality?
Zirconia powder quality is determined by specific standards set by various organizations. These standards include guidelines on purity, particle size, and chemical composition. International organizations like ASTM International and ISO provide these standards, which are crucial for industries relying on zirconia for manufacturing processes.
Compliance with these standards provides several advantages:
- Suitability for Applications: Ensures the powder meets the specific requirements for dental materials, industrial ceramics, and other applications.
- Product Credibility: Certified zirconia powder enhances the reputation of manufacturers and their offerings in the marketplace.
- Regulatory Compliance: Following these standards helps companies meet regional and international regulatory requirements.
The certification process typically involves rigorous testing and documentation. This process helps identify the legitimacy of suppliers and their products. Therefore, it is wise for companies to engage with accredited suppliers who follow these international quality standards.
| Standard Organization | Key Focus Areas | Certification Process |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM International | Purity, chemical composition | Regular testing |
| ISO | Quality management systems | Periodic audits |
| CE Marking | Compliance for European markets | Compliance verification |
What Testing Methods Validate Zirconia Powder Quality?
Testing methods play a crucial role in validating the quality of zirconia powder. Several techniques are commonly used to assess its properties.
One standard approach is the use of X-ray diffraction (XRD) to determine phase composition. This method helps identify any unwanted impurities present in the powder.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) offers insights into the surface morphology and particle size distribution. This visual inspection is essential for understanding how the powder will behave in manufacturing processes.
Other methods, such as energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), provide a detailed chemical analysis of the powder. This information is pivotal for ensuring that zirconia meets quality requirements.
Ultimately, a combination of these testing methods yields a comprehensive assessment of zirconia powder quality. They help not only in confirming compliance but also in providing feedback for potential improvements.
Some additional testing techniques include:
- Dynamic mechanical analysis (DMA) for temperature-related property changes.
- Laser diffraction for precise particle size measurements.
- Microhardness tests to assess surface hardness at small scales.
| Testing Method | Purpose | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray Diffraction | Phase composition | High precision, fast results |
| Scanning Electron Microscopy | Surface morphology and particle size | Detailed visual analysis |
| Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy | Chemical composition | Accurate elemental analysis |
How Do Physical Tests Assess Zirconia Powder?
Physical testing is vital for assessing the properties of zirconia powder. Several key attributes are measured to determine whether the powder will perform well in its applications.
Particle size distribution is one critical aspect, as it affects packing density and flowability. Tests like laser diffraction or sieve analysis are frequently employed to quantify this property.
Another essential measurement is bulk density, which gives insight into how the powder will compact and behave during sintering. High-quality zirconia should have consistent bulk density levels.
Additionally, flowability tests are conducted to ensure that the powder can be processed efficiently. Proper flow behavior is vital for maintaining productivity during manufacturing processes.
Examples of common flowability tests include:
- Cohesive and non-cohesive materials testing to determine how zirconia interacts with other substances.
- Funnel flow tests to assess the ease of powder movement from containers.
- Shear testing to measure powder behavior under stress.
In summary, physical tests provide essential data that informs suppliers and consumers about zirconia powder’s suitability for specific applications.
| Physical Property | Measurement Techniques | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Laser diffraction, Sieve analysis | Affects flow and quality |
| Bulk Density | Density measurement | Impacts packing and sintering outcomes |
| Flowability | Angle of repose tests | Ensures efficient processing |

This image depicts essential physical tests used to evaluate zirconia powder characteristics.
What Role Does Chemical Analysis Play in Testing?
Chemical analysis is a cornerstone of quality testing for zirconia powder. It examines the chemical composition of the powder to ensure it meets specified standards.
Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) is a common method for detecting trace elements. This analysis is crucial in industries like aerospace, where even minimal impurity levels can compromise product integrity.
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is another effective technique that allows for rapid and non-destructive analysis of zirconia powder. This method presents a clear picture of the elemental composition, helping to ensure material quality.
Moreover, chemical analysis helps manufacturers maintain compliance with regulatory guidelines, particularly for markets with strict material specifications.
Key components of a robust chemical analysis procedure include:
- Use of certified reference materials (CRMs) to ensure accuracy.
- Calibration of equipment to maintain precision.
- Implementing sample preparation protocols to reduce contamination risks.
In conclusion, thorough chemical testing not only confirms quality but also enhances the trust between suppliers and buyers, ensuring reliable and high-quality zirconia materials.
| Chemical Analysis Method | Application | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| ICP-MS | Trace element detection | High sensitivity and accuracy |
| XRF | Elemental analysis | Rapid and non-destructive testing |
Why Are Mechanical Tests Essential for Zirconia Powder?
Mechanical tests are essential for ensuring zirconia powder can withstand the demands of various applications. These tests measure properties like hardness, toughness, and strength.
One common mechanical test is the Vickers hardness test, which assesses how resistant the zirconia is to deformation. Higher hardness values indicate better durability, which is vital for applications like cutting tools.
Another key test is the bending strength test, which evaluates how well the zirconia can bear loads without breaking. This property is particularly important for applications in dental restorations.
Moreover, fracture toughness tests determine how resistant the zirconia is to crack propagation. Maintaining toughness while managing brittleness is critical for performance, especially in high-stress environments.
Mechanical properties that are often evaluated include:
- Yield strength, to determine maximum stress before deformation.
- Elongation, to assess how much the material can stretch before breaking.
- Compressive strength, which evaluates the powder’s ability to withstand axial loads.
Ultimately, these mechanical tests ensure that zirconia powder meets the performance expectations set by users, making them a vital component of quality assurance.
| Mechanical Property | Testing Method | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | Vickers hardness test | Durability for cutting tools |
| Bending Strength | Bending strength test | Load-bearing capacity |
| Fracture Toughness | Fracture toughness test | Resistance to crack propagation |
How Do Thermal Analysis Techniques Contribute to Quality?
Thermal analysis provides valuable insights into the thermal stability of zirconia powder. Such techniques help evaluate how zirconia behaves under high temperatures.
One common thermal analysis method is Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC). This technique measures heat flow associated with phase transitions in the powder. Identifying the temperature at which transformations occur is crucial for processing and application.
Another vital method is Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA), which assesses weight changes as temperature increases. This test helps identify decomposition points and other thermal stability characteristics.
Thermal behavior directly affects the end-use application of zirconia, especially in high-temperature environments. Understanding these properties ensures manufacturers can select the right zirconia grades for their needs.
Considerations for effective thermal analysis include:
- Proper sample preparation to ensure accurate results.
- Calibrating thermal analyzers to uphold measurement precision.
- Comparing results with industry standards to confirm quality.
Incorporating thermal analysis into quality testing not only enhances material performance but also reduces the risk of failures during application.
| Thermal Analysis Method | Purpose | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| DSC | Measure phase transitions | Critical for processing temperatures |
| TGA | Assess weight changes | Identifies decomposition points |
How Is Quality Assurance Implemented in Production?
Establishing a robust quality assurance framework is essential for maintaining the quality of zirconia powder throughout production processes. This involves setting clear quality benchmarks based on international standards.
Regular audits and inspections affirm compliance with these benchmarks. Engaging third-party auditors can add credibility to internal processes, as they provide an unbiased evaluation of the quality control measures in place.
Another key aspect is implementing statistical process control (SPC). This technique helps monitor production parameters in real-time, allowing for immediate adjustments if deviations occur. By tracking data trends, manufacturers can prevent quality issues proactively.
Additional best practices for effective quality assurance include:
- Documenting all procedures to ensure consistency in the quality control process.
- Implementing corrective actions swiftly when issues arise.
- Conducting regular training programs to keep staff informed on quality standards.
Additionally, fostering a quality-focused culture among the workforce is critical. Continuous training sessions for employees ensure everyone understands the importance of quality and stays updated on best practices.
In summary, a comprehensive quality assurance system not only ensures compliance but also drives continual improvement in production processes.
| Quality Assurance Element | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Regular Audits | Third-party evaluations | Objective insight into compliance |
| Statistical Process Control | Real-time monitoring | Prevents quality deviations |
| Employee Training | Continuous skill development | Maintains workforce awareness |
What Are Common Challenges in Testing Zirconia Powder?
Despite the best efforts to ensure high standards, several challenges persist in testing zirconia powder.
One challenge is dealing with impurities during the testing phase. These impurities can skew test results, leading to inaccurate assessments. Establishing strict sample preparation protocols can help minimize this issue.
Another difficulty lies in applying standardized methods across different testing labs. Variations in equipment and personnel can result in discrepancies in results. When working with multiple labs, it is crucial to have standardized procedures and calibration protocols in place.
Additionally, time and resource constraints can hinder thorough testing. Companies should plan for robust testing schedules to avoid rushed results, which can undermine quality assurance.
Some challenges that testers commonly face include:
- Maintaining equipment calibration to ensure accuracy.
- Training new personnel on testing procedures.
- Handling difficult sample types that may require special attention.
By recognizing and addressing these challenges, manufacturers can improve their testing processes, leading to more consistent quality in zirconia powder production.
| Common Challenge | Description | Proposed Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Impurities during testing | Can affect test accuracy | Strict sample preparation protocols |
| Standardization issues | Variability across labs | Establish standardized procedures |
| Resource constraints | Limited testing time | Adequate planning for testing timelines |

This image highlights the common challenges faced in quality testing of zirconia powder.
How Is Data from Testing Methods Reported?
Reporting data from testing methods is crucial for transparent communication between suppliers and buyers. Accurate and clear reporting enhances trust and enables informed decision-making.
Typically, reports should include detailed results from each test conducted, highlighting any deviations from expected values. This transparency is vital for validating quality assurance claims.
Additionally, certification documents play a significant role. These documents not only provide test results but also assure buyers of compliance with international standards.
Moreover, an executive summary should be included to provide an overview of the testing outcomes. This summary allows busy decision-makers to quickly grasp the quality status without delving into technical details.
Effective reporting practices should encompass:
- Consistent formatting for ease of understanding.
- A summary of key metrics that highlight compliance.
- Visual aids such as graphs to illustrate trends.
In short, well-structured data reporting ensures clarity and helps maintain productive relationships between companies and their suppliers.
| Report Component | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Detailed Results | Specific test outcomes | Validates quality and compliance |
| Certification Documents | Compliance assurance | Increases buyer confidence |
| Executive Summary | Overview of outcomes | Facilitates quick understanding |
What Future Trends Are Emerging in Zirconia Testing?
The future of zirconia testing is poised for significant advancements. These trends aim to enhance testing accuracy and efficiency.
Automation in testing processes is one notable trend. Automated systems can improve speed and consistency in performing various tests. This reduction in human error is essential for maintaining quality.
Another emerging trend is the incorporation of machine learning analytics. By analyzing historical testing data, machine learning algorithms can identify trends and predict potential quality issues.
Additionally, digital reporting platforms are gaining traction. These platforms streamline the reporting process, allowing for easier access and more user-friendly data presentation.
Future innovations that may enhance testing include:
- Integration of IoT devices for real-time monitoring in production.
- Enhanced simulation tools to predict material behavior before physical testing.
- Collaboration platforms for sharing testing results among partners.
As technology continues to advance, the testing of zirconia powder will become more efficient, accurate, and transparent. Companies investing in these developments can expect significant returns in quality assurance.
| Future Trend | Description | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Automation | Streamlined testing processes | Improved speed and consistency |
| Machine Learning | Data-driven insights | Predictive capabilities for quality |
| Digital Reporting Platforms | Enhanced data accessibility | User-friendly presentation of results |
Conclusion
In summary, this comprehensive exploration of testing procedures for zirconia powder emphasizes the importance of quality assurance throughout the production process. By understanding the wide array of testing methods—from physical and chemical analyses to mechanical evaluations—businesses can ensure they source high-quality materials. Quality inspections not only enhance end products but also reduce the risk of failures in their applications.
Engaging with Global Industry means taking practical steps toward excellence in sourcing zirconia. By leveraging established testing standards and emerging advancements, you can make informed decisions that benefit your bottom line. For more insights on best practices in material quality, consider reaching out for additional resources or professional guidance.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are the main properties of high-quality zirconia powder?
High-quality zirconia powder should exhibit excellent purity, typically greater than 99.5%, and controlled particle size, usually in the range of 0.1 to 1 micrometer, to ensure consistent behavior in applications. Additionally, its chemical composition should meet specific standards with minimal impurities, leading to superior mechanical and thermal properties essential for industrial applications.
Q2: Which industries rely on zirconia powder quality testing?
Zirconia powder is extensively used in industries such as ceramics, where it serves as a critical component for advanced ceramics and dental applications for prosthetics. The electronics industry utilizes it for its dielectric properties in capacitors, while the glass and metallurgy industries rely on zirconia’s thermal stability. Each of these sectors requires rigorous quality testing to ensure performance and reliability.
Q3: What are the costs associated with zirconia powder testing?
The costs of zirconia powder testing can vary widely depending on the methods selected and the extent of testing required. Basic physical and chemical analyses may cost less, while comprehensive testing involving advanced techniques like ICP-MS or XRD can be significantly more expensive. Additionally, costs might include laboratory fees, equipment maintenance, and the time required for testing, making it essential for companies to budget accordingly.
Q4: How often should zirconia powder undergo quality testing?
The frequency of quality testing for zirconia powder largely depends on production volume, application requirements, and regulatory standards. For continuous production processes, routine checks may be conducted daily or weekly. On the other hand, comprehensive tests should be performed periodically, such as monthly or quarterly, to ensure that suppliers meet quality benchmarks and that any variations in material properties are promptly addressed.
Q5: Can I conduct zirconia powder tests in-house?
Organizations with the necessary equipment and expertise can indeed conduct zirconia powder tests in-house. However, this requires investment in sophisticated testing instruments and thorough training for personnel. For smaller companies or those lacking resources, partnering with accredited laboratories is advisable. Such partnerships can provide access to advanced testing capabilities while ensuring compliance with industry standards and regulations.