When sourcing zirconia powder, understanding the quality control metrics that matter most is vital. Many decision-makers face challenges in ensuring their suppliers meet the required standards for consistency, performance, and reliability. This article aims to clarify the critical quality control parameters and their implications, providing practical insights that can enhance supplier assessment. You will gain trust in your purchasing decisions through informed criteria and practical examples, ensuring you choose the right zirconia powder supplier for your business needs.
What Are the Key Quality Control Metrics for Zirconia Powder?
Quality control metrics play a crucial role in evaluating zirconia powder suppliers. These metrics help ensure the material’s performance meets user expectations and industry standards.
The first metric to consider is purity. High-purity zirconia powder is essential for applications that require precision, such as dental materials and electronics. Impurities can compromise the material’s properties and lead to failures in use.
Next is particle size distribution. The size of the particles affects the performance of the powder in different applications. A consistent particle size contributes to uniformity in processes like milling and sintering.
Another vital metric is consistency. Suppliers should demonstrate the ability to produce zirconia powder with uniform characteristics over time. Variations can lead to unpredictable results in final applications, which can be costly for manufacturers.
Additionally, suppliers must provide compliance with standardized measurements. This adherence ensures that the powder produced meets regulatory requirements and can be reliably used in various industries.
Understanding these metrics will enable decision-makers to assess potential suppliers effectively. For example, if a supplier consistently shows high levels of purity and size uniformity, it signals their capability and commitment to quality.
| Metric | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | Amount of impurities present in zirconia | Ensures performance in critical applications |
| Particle Size Distribution | Range and uniformity in particle sizes | Affects packing, sintering, and overall quality |
| Consistency | Stability of properties over time | Reduces unpredictability in end-use results |
| Standardized Measurements | Compliance with industry standards | Guarantees product reliability and safety |
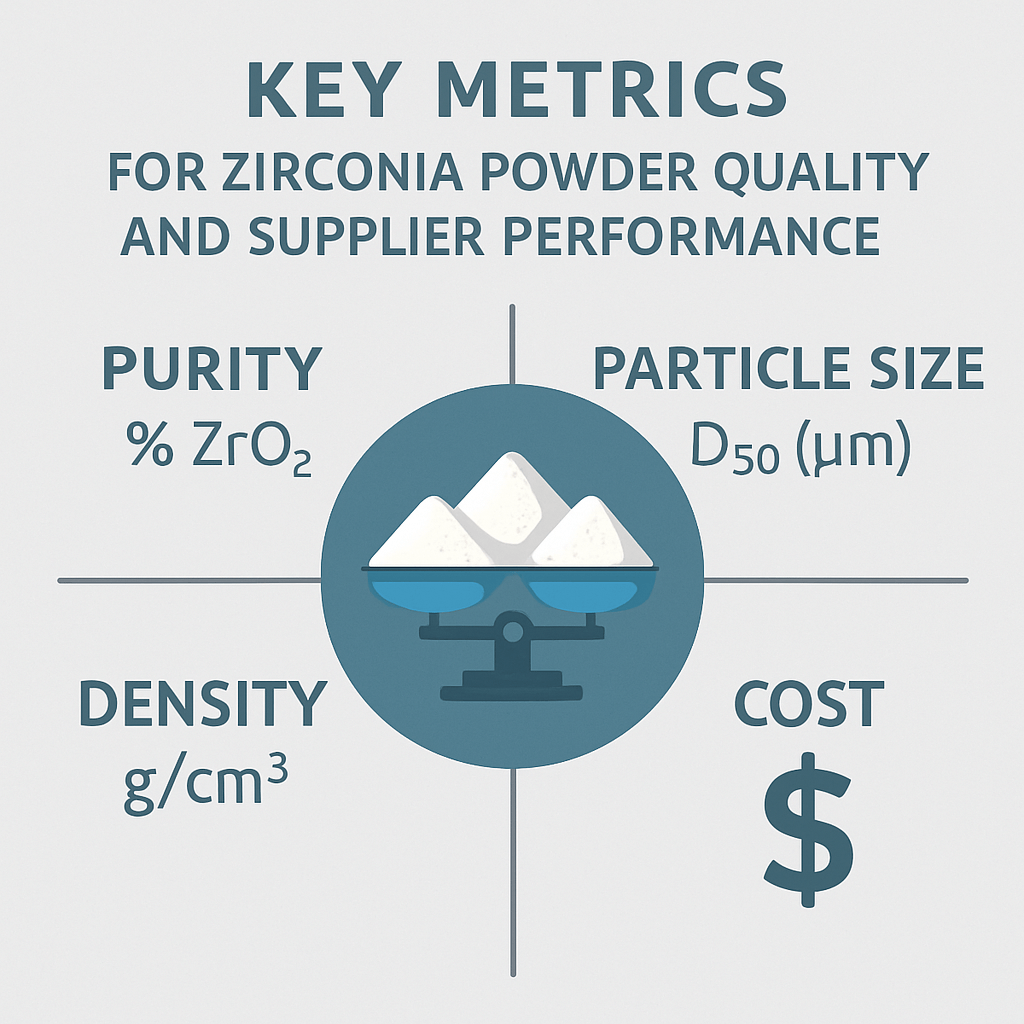
This image illustrates the critical metrics for evaluating zirconia powder quality and supplier performance.
How Do Supplier Certifications Affect Quality Control?
Supplier certifications offer assurance regarding the quality management processes in place. These certifications serve as a third-party validation of a supplier’s capabilities, making them an essential criterion in supplier evaluation. Certifications such as ISO 9001 indicate that a supplier adheres to recognized quality management principles, which include a focus on consistent quality, customer satisfaction, and continuous improvement.
For instance, freshly certified suppliers often undergo strict audits. These audits assess their processes, management systems, and compliance with quality standards. A rigorous certification process can help identify weaknesses and areas for improvement, thus ensuring that the zirconia powder produced meets predefined quality criteria.
In addition to ISO certifications, there are niche certifications relevant to specific industries, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices and ISO/TS 16949 for automotive suppliers. These certifications underscore a supplier’s commitment to quality and compliance with industry-specific regulations.
Furthermore, certified suppliers typically have robust internal processes to address quality issues proactively. They often invest in regular training for their teams, ensuring that staff members are knowledgeable about quality management and the latest industry standards. This constant focus on improvement not only enhances operational efficiency but also bolsters product reliability.
Consider these factors when evaluating certifications:
- The scope of the certification and whether it aligns with your industry needs
- The frequency of audits and updates to the certification
- The supplier’s history of compliance with quality standards
Ultimately, engaging with established suppliers that possess recognized certifications fosters a more robust supply chain and ensures high-quality products.
| Certification | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | Quality management systems | Ensures consistent quality and customer focus |
| ISO 13485 | For medical device production | Critical for industries requiring stringent controls |
| ASTM Standards | Various testing and material specifications | Guarantees reliability and safety in applications |
What Testing Methods Validate Zirconia Powder Quality?
To ensure the quality of zirconia powder, suppliers employ various testing methods. These tests validate the material’s characteristics and usability.
First, X-ray diffraction (XRD) is used to analyze the powder’s crystalline structure. This method helps ascertain the phase composition and detect impurities. A consistent crystal structure is vital for predictable mechanical properties.
Another important method is scanning electron microscopy (SEM), which provides detailed images of particle morphology. SEM can reveal surface defects and particle shapes that affect the performance of the zirconia powder.
Chemical analysis is equally essential. Techniques like inductively coupled plasma (ICP) spectroscopy determine the elemental composition of the powder. This step confirms whether the powder meets specified purity standards.
Lastly, mechanical testing assesses properties like hardness, bending strength, and toughness. These parameters are crucial for applications demanding durability and reliability.
Using these various testing methods, suppliers can guarantee the quality of their zirconia powder. For example, a supplier that regularly conducts XRD and mechanical testing demonstrates their commitment to providing high-quality products.
| Testing Method | Purpose | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray Diffraction (XRD) | Analyze crystalline structure and phase composition | Ensures purity and predicted material behavior |
| Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) | Assess particle morphology | Provides insight into potential performance issues |
| Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) | Determine elemental composition | Confirms adherence to purity standards |
| Mechanical Testing | Evaluate strength, toughness, and durability | Validates material for intended applications |
This image showcases the various testing methods used to validate the quality of zirconia powder, ensuring high standards.
How to Assess the Consistency of Zirconia Powder Production?
Assessing production consistency involves analyzing several factors that can affect the zirconia powder’s properties. Consistency is not just about maintaining uniformity; it’s also about ensuring that each batch meets quality expectations throughout the manufacturing process.
First, process control is paramount. Suppliers should implement strict protocols for monitoring the manufacturing process. This involves tracking variables like temperature, pressure, and mixing times to ensure uniform results. Regular audits of these processes can help identify areas for improvement, fostering an environment of continuous quality enhancement.
Additionally, batch testing plays a crucial role. Suppliers should conduct tests on every batch produced, as even small variations can lead to significant differences in product performance. This approach helps mitigate risks associated with inconsistencies, providing greater assurance to buyers about product reliability.
It’s also essential for suppliers to maintain detailed production records. Implementing a robust documentation system allows tracking of every production detail, such as raw material sources and handling processes. These records can provide insights into historical performance and help identify trends or issues that may affect consistency.
Moreover, to enhance consistency, suppliers may adopt strategies such as:
- Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs): Establishing clear guidelines for each step in the production process ensures that all personnel follow the same methods.
- Regular Training: Providing ongoing training for employees helps maintain high standards of workmanship and awareness of quality control practices.
- Quality Control Checkpoints: Implementing specific points in the manufacturing process where quality checks occur can catch deviations early, preventing larger issues later.
For example, a supplier that includes batch testing and detailed documentation in their quality control procedures demonstrates an understanding of the complexities involved in maintaining consistency. This thoroughness not only assures the purchaser of quality but also instills confidence in the overall reliability of the supply chain.
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Process Control | Monitoring of production variables | Ensures uniform production |
| Batch Testing | Testing every production batch | Prevents quality variations |
| Production Records | Documentation of all production details | Aids in identifying trends and quality issues |
By implementing these measures, suppliers can better manage production consistency, ultimately resulting in higher quality zirconia powder that meets customer expectations and application requirements.
Why Is Particle Size Distribution Critical in Quality Control?
Particle size distribution is a key quality attribute in zirconia powder. It plays a significant role in the material’s performance across various applications, influencing not only the end product’s quality but also the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
A well-controlled particle size distribution enhances flowability and packing density. This is particularly important in processes like sintering, where consistent green density contributes to optimal results and final product strength. If the size distribution is not within specified limits, it can lead to issues such as uneven packing, which subsequently affects sintering behavior and mechanical properties.
Furthermore, the final properties of ceramics are highly influenced by particle size. Smaller particles generally lead to denser structures with improved mechanical strength, as they can fill voids better during the consolidation process. Conversely, larger particles may result in decreased strength and increased brittleness, which can be detrimental in load-bearing applications.
To maintain ideal particle size distribution, suppliers should utilize techniques like laser diffraction analysis. This method provides accurate sizing measurements, allowing for timely adjustments to achieve desired characteristics. Regular monitoring through such methods ensures that the material consistently meets performance standards.
It’s also important to note that selecting the right particle size is not just about achieving immediate performance objectives. It has long-term implications for product reliability and durability. Therefore, suppliers should prioritize quality control measures that focus on maintaining optimal particle size distribution.
Key considerations for suppliers regarding particle size distribution:
- Regular Particle Size Testing: Frequent assessments help maintain consistency and detect deviations early.
- Understanding Application-Specific Requirements: Different applications may require different size distributions to achieve optimal performance.
- Adjustments Based on Feedback: Gathering performance data from end-users can inform adjustments to size distribution strategies.
| Size Distribution Type | Description | Application Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Narrow Distribution | Minimal variation in particle sizes | Enhances flowability and sintering properties |
| Wide Distribution | Greater variation in sizes | Can lead to uneven performance |
What Role Does Purity Play in Quality Control for Zirconia Powder?
Purity is a fundamental quality metric that significantly influences the performance of zirconia powder across various applications.
High-purity zirconia powder is essential for applications such as dental ceramics, electronics, and bio-ceramics. In these fields, even minor levels of contaminants can adversely affect mechanical properties, such as strength and durability. For instance, impurities might lead to discoloration in dental applications, undermining aesthetic appeal, or result in reduced electrical properties in electronic components.
To ensure purity, suppliers can implement rigorous cleaning and purification steps throughout their production processes. Some common practices include:
- Washing Raw Materials: This step helps eliminate contaminants before they enter the production line, significantly improving the final product’s quality.
- Advanced Production Techniques: Employing methods such as high-temperature processing can help break down and remove unwanted elements.
- Frequent Quality Testing: Regularly conducting purity assessments through methods like X-ray fluorescence (XRF) or thermal analysis ensures that the material meets specified purity standards.
Furthermore, employing advanced analytical techniques like thermal gravimetric analysis can help identify any remaining impurities that may affect performance. A commitment to high purity in zirconia powder production can demonstrate a supplier’s focus on quality and performance. As a case in point, a supplier known for stringent purity measures builds trust with buyers seeking reliable materials.
| Purity Characteristics | Importance | Techniques for Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Low Impurity Levels | Ensures optimal performance | X-ray fluorescence, thermal analysis |
| Regular Purity Testing | Maintains adherence to specifications | Routine analytical assessments |
Overall, prioritizing purity in zirconia powder is not just about meeting specifications; it is about ensuring that the end products perform reliably and consistently in their intended applications.
How Can Traceability Improve Zirconia Powder Quality Assurance?
Traceability is critical in establishing a robust quality assurance system for zirconia powder suppliers. It allows for the complete tracking of material from its source through to the final product. By maintaining thorough documentation at each stage of the production process, suppliers can provide comprehensive records that include the origin of raw materials, manufacturing conditions, and quality control tests performed.
This systematic approach enhances accountability. If a quality issue arises down the line, traceability enables stakeholders to pinpoint where the problem occurred. For instance, if a batch exhibits defects, identifying the specific raw material or production method that led to the issue can facilitate quick remedial actions. This capability reduces risks and fosters confidence in the supply chain.
Moreover, traceability encourages suppliers to maintain high standards of quality control. Awareness that their processes are subject to scrutiny compels them to adhere to strict quality measures and regulatory requirements. It also promotes transparency with clients, allowing them to feel more secure about the materials they are sourcing.
In addition to tracking materials, it’s beneficial for suppliers to conduct regular audits of their processes. This ensures compliance with established quality standards and helps identify potential areas for improvement.
Key elements that enhance traceability include:
- Documented processes: Clear records of all production stages.
- Batch identification: Unique identifiers for each production batch to track history.
- Supplier relationships: Strong partnerships with raw material providers to ensure quality upstream.
Suppliers that prioritize traceability present their operations as trustworthy and reliable. This not only protects their customers but also upholds their reputation in a competitive marketplace.
| Traceability Element | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Documentation | Complete records of production processes | Facilitates quick identification of issues |
| Material Tracking | Ability to trace raw materials back to suppliers | Enhances accountability and transparency |
What Are Common Defects in Zirconia Powder and Their Causes?
Quality control processes seek to minimize defects in zirconia powder. However, understanding common defects is essential for effective supplier evaluation.
One common defect is agglomeration. This occurs when particles clump together, affecting flow and uniformity. Agglomeration can result from improper storage conditions or moisture exposure.
Another issue is non-uniform particle sizes. Variability in size can lead to unpredictable results in applications. It may stem from inadequate milling or classification processes.
Finally, contamination can compromise powder quality. This may happen when materials are not stored properly or the manufacturing equipment is not cleaned thoroughly.
Identifying these potential defects in suppliers can help you make informed decisions. A supplier with a clear approach to preventing defects demonstrates their commitment to quality and reliability.
| Common Defect | Description | Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Agglomeration | Clumping of particles | Improper storage or moisture exposure |
| Non-uniform Particle Sizes | Variability in particle dimensions | Inadequate milling or classification |
| Contamination | Presence of unwanted substances | Poor storage practices |
How to Evaluate Supplier Quality Control Processes?
Evaluating supplier quality control processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Start by reviewing their quality management systems. A robust system should outline how the supplier monitors and maintains product quality throughout the production process.
Next, request quality reports and documentation. These provide insights into their testing methods, frequency of evaluations, and results over time. Look for consistent performance across batches.
Site visits can also offer valuable perspectives. Directly observing quality control procedures can help you assess the supplier’s commitment to meeting quality standards.
Lastly, engage with past clients to gather feedback on their experiences with the supplier. This firsthand information can illuminate the supplier’s reliability and responsiveness to quality issues.
By evaluating these aspects, you can identify suppliers that prioritize quality and reliability, ultimately benefiting your business.
| Evaluation Criterion | Purpose | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Quality Management Systems | Understanding of quality processes | Indicates commitment to quality |
| Quality Reports | Analysis of testing methods | Assesses supplier performance over time |
| Site Visits | Direct observation of quality control | Provides real-time insights into operations |
| Client Feedback | Insight into supplier reliability | Builds a fuller picture of company reputation |
What Should You Look For in a Quality Agreement?
A well-structured quality agreement is vital for establishing clear expectations between businesses and suppliers.
Start by ensuring that the agreement outlines specific quality metrics. These metrics should include definitions of what constitutes acceptable quality related to purity, size distribution, and more.
Next, include responsibilities. Each party should know what is expected regarding quality control measures and reporting.
It’s also beneficial to establish consequences for non-compliance. Laying out clear repercussions for failing to meet specifications ensures accountability.
Regular review of the agreement can help address changing needs and expectations. This ongoing dialogue can facilitate improvements and foster a strong partnership.
A strong quality agreement aligns the goals of both parties, facilitating better collaboration and outcomes.
| Agreement Element | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Defined Quality Metrics | Clear standards for assessment | Reduces ambiguity and enhances alignment |
| Specified Responsibilities | Outline of obligations for both parties | Promotes accountability and transparency |
| Consequences for Non-Compliance | Clear repercussions for unmet standards | Encourages adherence to quality expectations |
Conclusion
In summary, understanding the essential quality control metrics for evaluating zirconia powder suppliers is critical. Key factors include purity, particle size distribution, and supplier certifications, impacting the material’s performance and reliability. A clear advantage of mastering these metrics is the ability to make informed decisions that reduce risks in procurement. For purchasers seeking reliable zirconia powder, consider collaborating with Global Industry. Leveraging our expertise can elevate your supplier assessments and ensure exceptional quality.
FAQ Section
Q1: What are the most common quality control metrics for zirconia powder?
The most common quality control metrics include purity, particle size distribution, consistency, and standardized measurements. Purity ensures the absence of undesirable impurities, while particle size distribution affects the powder’s flow properties and application performance. Consistency guarantees uniformity over time, and adherence to standardized measurements ensures compliance with industry regulations.
Q2: Why is certification important in supplier evaluation?
Certifications are crucial as they affirm that suppliers comply with recognized quality management standards, such as ISO 9001. This compliance signals a commitment to quality processes and customer satisfaction. Suppliers with certifications are more likely to maintain high production standards, reducing risk for buyers by ensuring the zirconia powder meets safety and quality specifications.
Q3: How can I ensure consistent quality from my zirconia powder suppliers?
To ensure consistent quality, buyers should conduct regular assessments of supplier practices, including audits of their quality control systems. Establishing clear quality expectations through contracts, frequent communication, and maintaining an ongoing dialogue can help. Additionally, requesting batch reports and performance metrics can provide insights into the supplier’s adherence to quality standards.
Q4: What are the potential defects found in zirconia powder?
Common defects include agglomeration, which leads to clumping and inconsistent particle sizes, affecting flowability. Non-uniform particle sizes can result from inadequate milling or blending processes, impacting the final product’s performance. Contamination from external sources or improper storage can introduce undesirable materials, potentially compromising application integrity and durability.
Q5: How does traceability enhance quality assurance in zirconia powder sourcing?
Traceability allows manufacturers to track all materials used in the production of zirconia powder, creating a clearer link between the source and the end product. This systematic tracking enhances accountability, enabling manufacturers to quickly identify and address any quality issues that arise. Transparency in the supply chain builds trust between buyers and suppliers, promoting consistent quality assurance practices.