Choosing the right Zircon Sand grade affects product quality more than many buyers realize. Using the wrong grade can cause surface cracks, dull finishes, or even defective castings. Many purchasing teams still mix up technical specs with price and face costly mistakes later. This guide clears the confusion. It covers how Zircon Sand grades differ, where they come from, and what steps top buyers follow to protect their budgets. Backed by industry experience, this advice helps you pick, test, and store Zircon Sand with confidence.
What Makes Zircon Sand Grades Different?
Understanding Key Quality Factors
Zircon sand grading depends mostly on chemical purity, grain size consistency, and trace mineral content. High-grade batches show over 65% ZrO₂ with minimal iron or clay. Lower grades drift closer to 60% or less, sometimes with more unwanted particles. These details determine whether your ceramics glaze smoothly or crack after firing.
Real-World Example: Cost of Wrong Grade
One large ceramic floor tile producer in Southeast Asia bought mid-grade sand for a new premium tile line. Within six months, customer complaints about pinholes and rough finishes soared by 25%. After testing, engineers confirmed inconsistent grain sizes and lower purity were the cause. Switching to a verified premium grade reduced scrap and refunds by more than 15% within two production cycles.
Technical Breakdown
- Chemical Purity: Directly impacts melting point and finish quality.
- Grain Size: Affects flow in molds and glaze smoothness.
- Trace Minerals: More iron or clay can ruin color consistency.
Buyer Tip
Always request a COA (Certificate of Analysis) with each batch, and cross-check with your own lab before full production starts.
| Grade | ZrO₂ Content (%) | Typical Use | Average Batch Size (tons) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premium | 65%+ | Glossy tiles, advanced refractories | 20–50 |
| Standard | 62–65% | Foundry castings, general refractories | 50–150 |
| Low | Below 62% | Low-end casting fillers, road base | 150–400 |
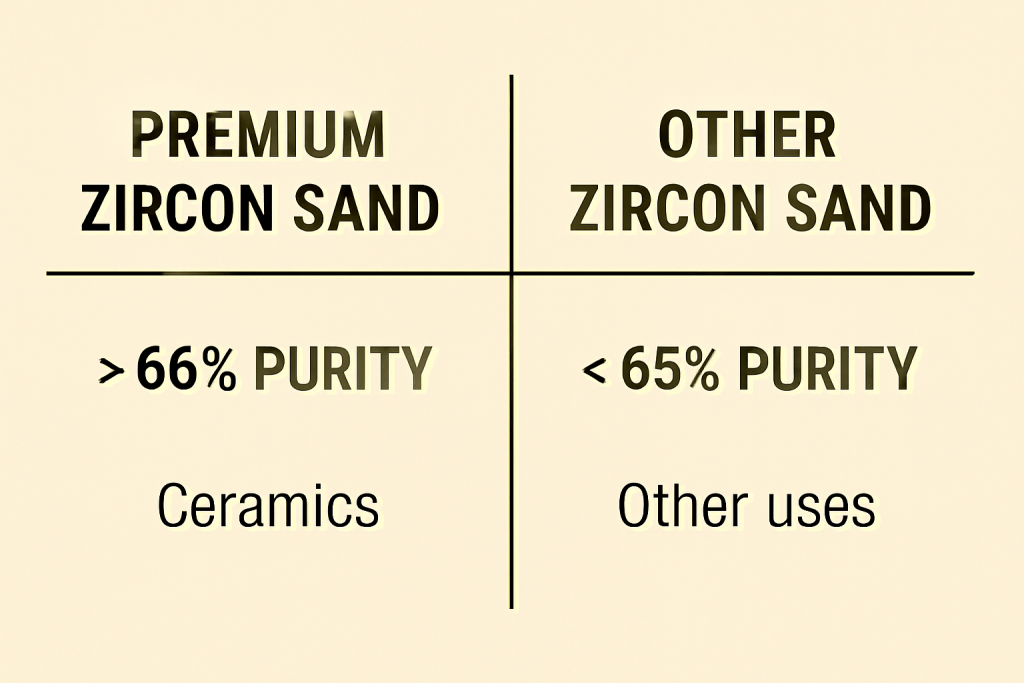
Visual comparing the chemical purity and best-fit use for each zircon sand grade to aid buyer decisions.
How Do Suppliers Classify Zircon Sand?
Methods Used by Trusted Exporters
Top suppliers rely on certified labs and standardized processes. Core checks include sieve analysis for grain size distribution, X-ray fluorescence (XRF) for chemical breakdown, and moisture tests to guarantee dry shipment.
Most reputable mines comply with ISO 9001 for quality and ISO 14001 for environmental handling. These certificates reassure buyers that extraction and packaging meet global standards.
Real Buyer Practice
One European foundry group requires an independent lab to check random containers on arrival, not just the supplier’s own COA. This double-check stops disputes before production begins.
Classification Steps
- Sieve Analysis: Confirms grain range matches ordered specs.
- XRF Scanning: Detects real ZrO₂ level and any unwanted metals.
- Moisture Control: Keeps bags dry and free-flowing.
Supplier Checklist
Before placing a large order, confirm:
- Does the mine provide lab credentials?
- Are third-party results available?
- How are rejected lots handled?
| Test | What It Checks | Why It Matters | Pass Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sieve | Grain spread | Smooth casting flow | 95% in target mesh |
| XRF | ZrO₂ and impurities | Performance predictability | 65%+ ZrO₂ |
| Moisture | Dampness | Prevents storage clumps | Below 0.5% |
What Are the Top Grades Available Globally?
Major Commercial Grades Explained
Buyers usually pick from three broad groups: premium, standard, and low. Premium suits strict ceramic glaze lines where even minor defects mean customer returns. Standard fits most foundry molds and everyday castings. Low grade often mixes with fillers for construction or road materials.
Impact of Market Conditions
Economic swings, shipping costs, and mining output shifts affect grade availability. For instance, new environmental laws in Australia reduced mining hours last year, pushing premium prices up by 12%. Smart buyers maintain buffer stock to ride out price peaks.
Buyer Insight
A Taiwanese sanitaryware producer contracts two suppliers for premium grade but tests smaller lots from new mines during off-peak season to get better rates without risking main production.
| Grade | Typical Buyer | Common Supply Terms | Typical Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| Premium | Ceramic plants, chemical refineries | Contract + spot | 30–50 days |
| Standard | Foundries, bulk molders | Spot purchase | 15–30 days |
| Low | Road works, filler suppliers | Bulk only | 10–20 days |
This map shows main export regions, helping buyers plan sourcing across suppliers.
Where Do High-Quality Grades Come From?
Key Mining Regions
The purest zircon sand typically comes from Australia, South Africa, and Mozambique. Australian grades lead the market for tight ZrO₂ control and reliable year-round output. South African mines deliver large volumes, although purity can vary across different pit zones.
Regional Export Hurdles
Weather plays a big role. For example, Mozambique’s rainy season can swamp roads, delaying bulk truck shipments to ports. Savvy buyers negotiate backup storage near docks to hold buffer stock.
Case: Risk Diversification
A big ceramics factory in Malaysia once depended on a single mine in Western Australia. Floods hit rail lines for three weeks, halting raw material flow. Since then, the company splits its orders: 70% from Australia, 30% from South African or local traders for fast top-up.
Logistics Tip
Always check port capacity and customs speed. Delays at small ports can eat savings from low-cost mines.
| Region | Key Advantage | Top Buyers | Known Issues |
|---|---|---|---|
| Australia | Consistent ZrO₂ | High-end ceramics | Tight export controls |
| South Africa | High capacity | Foundries, bulk traders | Grade swings |
| Mozambique | Growing supply | Flexible contracts | Road floods |
Which Industries Rely on Different Grades?
Primary Applications
Every sector has its must-have specs. Tile makers chase whiteness and smooth finish. Refractory producers need grains that withstand extreme furnace heat. Foundries favor cost balance: good enough flow without overpaying.
Buyer Insight
A purchasing head for a Spanish tile line says, “Cheap sand may look fine on paper, but rejects at the end of firing eat profit twice as fast. I’d rather pay more upfront.”
Sample Monthly Demand
| Industry | Ideal Grade | Core Need | Avg Monthly Volume |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tiles & Sanitaryware | Premium | Perfect glaze | 300–500 tons |
| Refractories | Premium | High thermal shock resistance | 200–400 tons |
| Foundries | Standard | Mold fill speed | 500–800 tons |
| Construction Fill | Low | Bulk, non-critical | 1000+ tons |
Buyer Tip
Before signing a full-year contract, request a pilot lot. Test it under real production for at least one full cycle.
How Does Grade Influence Price and Supply?
Price Tiers and Volatility
Zircon sand prices swing with mining conditions, energy costs, and shipping lane stability. Premium grades cost the most due to tighter quality control and limited deposits. Standard grades offer a fair balance between cost and performance. Low grades stay cheap but can bring higher reject rates, so hidden costs pop up in rework.
A quick story:
A foundry in Poland bought discount mid-grade sand during a supply crunch. Mold cracks rose by 20% that quarter. Savings on raw materials vanished under scrap costs and extra labor.
Five-Year Market Trend
This trend table shows typical spot prices for premium and standard grades. Note that weather events, labor strikes, or port slowdowns can shift these figures overnight.
| Year | Premium ($/ton) | Standard ($/ton) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 1,750 | 1,400 | – |
| 2020 | 1,900 | 1,500 | +8% |
| 2021 | 2,050 | 1,600 | +7% |
| 2022 | 2,200 | 1,750 | +8% |
| 2023 | 2,100 | 1,680 | -5% |
Contract vs. Spot Orders
Long contracts lock better rates but limit flexibility. Many buyers combine them with spot purchases to stay nimble when market dips occur.
Buyer Tip
Include price adjustment clauses for fuel or shipping spikes in long-term deals.
What Should Buyers Check Before Purchasing?
Buyer’s Pre-Order Checklist
Skipping checks risks downtime and spoiled batches. Smart teams share this internal checklist before approving any bulk shipment.
- Confirm Certificate of Analysis
- Demand recent third-party lab result
- Verify mine licenses and compliance records
- Check shipment packing style (double bagging helps)
- Agree on Incoterms and dispute process in writing
Common Pitfall: Overreliance on Agent Promises
One buyer in the Middle East trusted an unknown broker. Sand arrived 12% under promised ZrO₂, and legal recovery took eight months.
Internal Tip
Train your warehouse crew to reject torn bags on arrival and report moisture right away.
| Step | Key Purpose | Result |
|---|---|---|
| COA | Matches order specs | No surprises |
| Third-party test | Confirms purity | Added security |
| Legal docs | Prevents fraud | Traceable supply |
| Double bagging | Blocks leaks | Cleaner storage |
How Can Buyers Store Zircon Sand Properly?
Proper Bulk Storage
Once your premium sand lands at port, bad storage can ruin it before production even starts. Moisture causes lumps, hard spots, and inconsistent flow in hoppers.
Industry practice:
Modern warehouses store bulk bags on pallets, off concrete floors, with clear aisle spacing for airflow. Humidity gauges run 24/7.
Handling Tips for Big Volumes
Rotate old bags forward. Seal partially used bags quickly. In humid regions, some buyers install portable dehumidifiers or silica gel packs inside big bag liners.
| Storage Action | Why It Matters | Practical Result |
|---|---|---|
| Use pallets | Avoids wet floor contact | Dry, easy handling |
| Rotate stock | Keeps grains fresh | No lumps |
| Monitor humidity | Spots leaks early | Smooth hopper flow |

Dry, raised storage ensures top-grade sand keeps its quality until last batch is used.
What Are Sustainable Sourcing Practices?
Buyers Expect More than Cheap Sand
Responsible buyers look beyond price. Many large importers now audit mines for fair labor, safe disposal, and land rehab plans.
Example of Responsible Mining
One Mozambique miner now converts old pits into community farming ponds. Villagers raise fish or irrigate crops, turning depleted land into food hubs.
What to Ask Your Supplier
- Do they restore mined land?
- Any certified environmental plan?
- Proof of safe waste handling?
Buyer Tip
A visible green supply chain can win trust from big customers downstream, especially European and North American buyers.
| Practice | Community Gain | Buyer Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Land rehab | Fish farms | Local support |
| Legal mining | Tax stability | Uninterrupted supply |
| Green seal | Meets regulations | Better brand reputation |
What Trends Are Shaping Grade Demand Today?
Demand Shifts by Region
Asia’s urban building boom means steady appetite for premium tiles. Foundry markets in Europe stay level but watch costs closely. Africa increases mining sites, yet port issues can limit bulk exports.
Forecast Snapshot
Over the next two years, Asia’s tile sector could lift premium sand need by 5–6% yearly. Some buyers expect extra taxes on raw sand to push price floors higher.
| Region | 2-Year Demand Change | Buyer Action |
|---|---|---|
| Asia | +5% yearly | Lock more premium contracts |
| Europe | Stable | Negotiate long deals |
| Africa | +10% capacity | Spot deals possible |
Buyer Insight
Plan ahead when new plants open — sudden large orders stress even stable mines.
Conclusion
Choosing the right zircon sand grade brings steady output, clean finishes, and lower waste. Smart buyers stay informed on grade specs, source diversity, and changing costs. These steps protect your supply chain and factory uptime. Ready to get secure, tested supply? Reach out to Global Industry today for a clear quote and custom advice for your plant. We stand by your goals with reliable sand and expert support, batch after batch.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is zircon sand mainly used for?
Zircon sand finds heavy use in ceramics for glazes and tiles, refractories for high-temperature bricks and linings, foundry molds for casting metal parts, and sometimes in chemicals for producing zirconium compounds. Its stable heat resistance and low chemical reactivity make it a trusted base material in these sectors.
Q2: How can I verify a supplier’s grade claims?
Always request a fresh Certificate of Analysis (COA) for each shipment and cross-check that the ZrO₂ content, grain size, and impurity levels meet your contract specs. Many reliable buyers also order third-party lab tests or hire inspection agencies to witness loading and sample sealing to avoid shipment swapping or quality drift.
Q3: Are there substitutes for high-grade zircon sand?
Some foundries and low-end ceramic makers switch to lower-grade sands, recycled sand, or even cheaper minerals like silica when budgets tighten. However, this often lowers product quality or causes more rejects. For critical applications where purity and heat resistance matter most, substitutes rarely match zircon’s performance.
Q4: How does storage affect zircon sand quality?
Moisture and contamination pose the biggest threats. Damp sand clumps together, blocks feeders, or affects mixing ratios. Dust, metal shavings, or organic debris may enter bags if storage areas lack covers or pallet racks. Always store in sealed bins or bulk bags raised off the floor, and monitor warehouse humidity to keep the sand free-flowing.
Q5: Why does the grade impact final product quality?
Grades determine how pure the sand is and how consistently it behaves during firing or casting. Premium grades lead to smoother ceramic glazes, higher brick strength, and fewer defects in metal molds. Lower grades can carry more impurities that cause color spots, weak points, or shape deformation, leading to more scrap and higher production costs over time.