In the competitive ceramics market, achieving the right glaze whiteness is critical for manufacturers looking to establish a strong place in the industry. Many producers face recurring challenges, such as insufficient whiteness that impacts the aesthetic and functional qualities of their products. Additionally, with rising raw material costs and increased consumer demands for higher quality, profit margins can become tighter than ever. So, how can this particular ingredient help solve these pressing issues?
This article will explore the multifaceted benefits of utilizing zirconium silicate, providing actionable insights into their selection and application within ceramic glazes. Focusing on practical and effective strategies, we aim to aid manufacturers in enhancing their product lines while maintaining cost-effectiveness. With expert knowledge at your disposal, you can confidently navigate the complexities of improving glaze whiteness for your ceramic products.

This image showcases various ceramic glaze samples, highlighting the importance of whiteness and color uniformity in ceramics.
Why Do Ceramic Products Struggle with Glaze Whiteness?
Ceramic manufacturers frequently encounter significant challenges related to glaze whiteness, which is crucial for creating visually appealing products. The aesthetic properties of ceramics significantly impact consumer preferences. When potential buyers select ceramic items, they often prioritize bright, uniform colors. Insufficient whiteness can tarnish the reputation of a brand and lead to disappointing sales figures.
Moreover, various factors contribute to these challenges. For instance, the quality of raw materials plays a vital role. If raw materials contain contaminants or impurities, they can adversely affect the glaze’s final appearance. Additionally, the manufacturing process itself is critical. Factors such as mixing procedures, firing temperatures, and kiln atmospheres can either enhance or detract from the whiteness of the glaze. For many producers, these challenges can lead to frustration and financial loss, as rework and waste can further squeeze profit margins.
As manufacturers strive to adapt to market demands, the implementation of zirconium-based compounds presents an effective solution to improve the whiteness of ceramic glazes. Through precise formulation and application of zirconium silicate, businesses can address these challenges head-on, elevating the quality of their products while optimizing processes to minimize costs. This article aims to illuminate how leveraging this powerful ingredient can serve as a game-changer for the ceramics industry, leading to tangible improvements and enhanced customer satisfaction.
How Does Zirconium Silicate Address These Issues?
Zirconium silicate serves as a pivotal component in producing superior ceramic glazes. Its unique properties not only enhance aesthetic appeal but also offer performance benefits that address several common manufacturing challenges.
First and foremost, zirconium silicate significantly improves the whiteness and opacity of glazes. This is largely due to its high refractive index, which allows for superior light interaction. When manufacturers add this compound to their glaze formulations, they often notice a marked increase in the visual brilliance of the final product. The result is a more appealing surface that attracts customers who prioritize appearance when selecting ceramics.
Moreover, zirconium silicate exhibits remarkable chemical stability during high-temperature firing processes crucial to ceramic production. This stability is essential at elevated temperatures, where many other materials might decompose or interact unfavorably with other glaze components. Consequently, incorporating this compound helps maintain color consistency and prevents unwanted changes that could compromise both aesthetics and performance.
Additionally, the use of zirconium-based formulations enhances the overall physical properties of ceramic glazes. This includes improved hardness, resistance to wear, and greater durability. When glaze provides better protection against scratches, stains, and chemical corrosion, the resulting ceramics deliver higher quality and longer-lasting products. Such enhancements not only elevate the standing of ceramic goods but also improve efficiency by lowering reject rates during production.
In summary, the integration of zirconium silicate into ceramic glazes offers manufacturers a robust solution to boost glaze whiteness, enhance durability, and ensure consistent quality. The multifaceted advantages make it a vital ingredient for businesses seeking to elevate their product offerings in a competitive market.
What Are the Key Advantages of Zirconium Silicate?
Utilizing zirconium-based compounds in ceramic glaze formulations comes with several distinct advantages that set them apart from alternative whiteners or additives.
Exceptional Whitening and Opacifying Effects
One of the standout features of zirconium silicate is its ability to provide exceptional whitening and opacifying effects. With a high refractive index, it achieves superior light scattering, resulting in a glossier and more vibrant appearance compared to standard whiteners. When used in glazes, products often exhibit enhanced brightness and depth of color, making them much more visually appealing to consumers.
| Feature | Standard Whitener | Zirconium Compound |
|---|---|---|
| Refractive Index | Lower | Higher |
| Opacity | Moderate | Excellent |
| Brightness | Dull | Brilliant |
Remarkable Chemical Stability
Another critical advantage lies in the chemical stability of zirconium silicate at high firing temperatures. Other glaze components can break down under extreme conditions, altering colors or decreasing the effectiveness of the glaze. However, zirconium-based materials resist decomposition, ensuring that the desired hues remain intact even after rigorous firing cycles.
Enhanced Physical Properties
This particular material also enhances the physical characteristics of the glaze itself. When used effectively, it contributes to improved hardness, higher durability, and better resistance to chemical corrosion. These properties become evident in the quality and longevity of ceramic products, leading to increased customer satisfaction and potentially higher sales.
Cost-Effectiveness and Financial Implications
While zirconium compounds may come with a slightly higher price tag than more common alternatives, the return on investment becomes clear through their efficiency. Due to their strong performance, manufacturers often need to use less of this compound in their formulations. Therefore, despite the initial materials cost, companies benefit from reduced waste, fewer defects, and a higher percentage of first-quality products.
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Application Cost | Low usage amounts | Initial material cost higher |
| Waste Reduction | Decreased defects | – |
| Overall Quality | Higher grade items produced | – |
How Should Zirconium Silicate Be Selected for Use?
The selection of zirconium compounds is critical for maximizing their benefits within glaze formulations. When integrating this ingredient, various parameters must be considered to ensure optimal performance.
Choosing the Right Particle Size
Particle size plays a significant role in the effectiveness of zirconium in glazes, measured using the D50 metric, referring to the average particle size. Smaller particles tend to yield a smoother glaze finish, making them suitable for high-end porcelain products, while coarser particles can be used for standard ceramics. Manufacturers often find that fine-grained zirconium silicate not only provides better whiteness but also helps achieve a more uniform surface, contributing to the overall quality of the finished product.
Selecting Optimal Purity Levels
Another important consideration is the purity level of zirconium silicate. Purity commonly varies such as 63%, 64%, or 65%. Higher purity typically results in better performance, particularly concerning color brightness. However, manufacturers must weigh the benefits against the potential cost implications.
| Purity Level | Appearance Quality | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 63% | Moderate | Lower |
| 64% | Good | Moderate |
| 65% | Excellent | Higher |
Important Considerations on Radioactivity
In addition to purity, ensuring low radioactivity in zirconium formulations is essential, especially for consumer goods like tableware and sanitary ceramics. Using products with certified low radioactivity helps maintain safety standards and consumer trust.
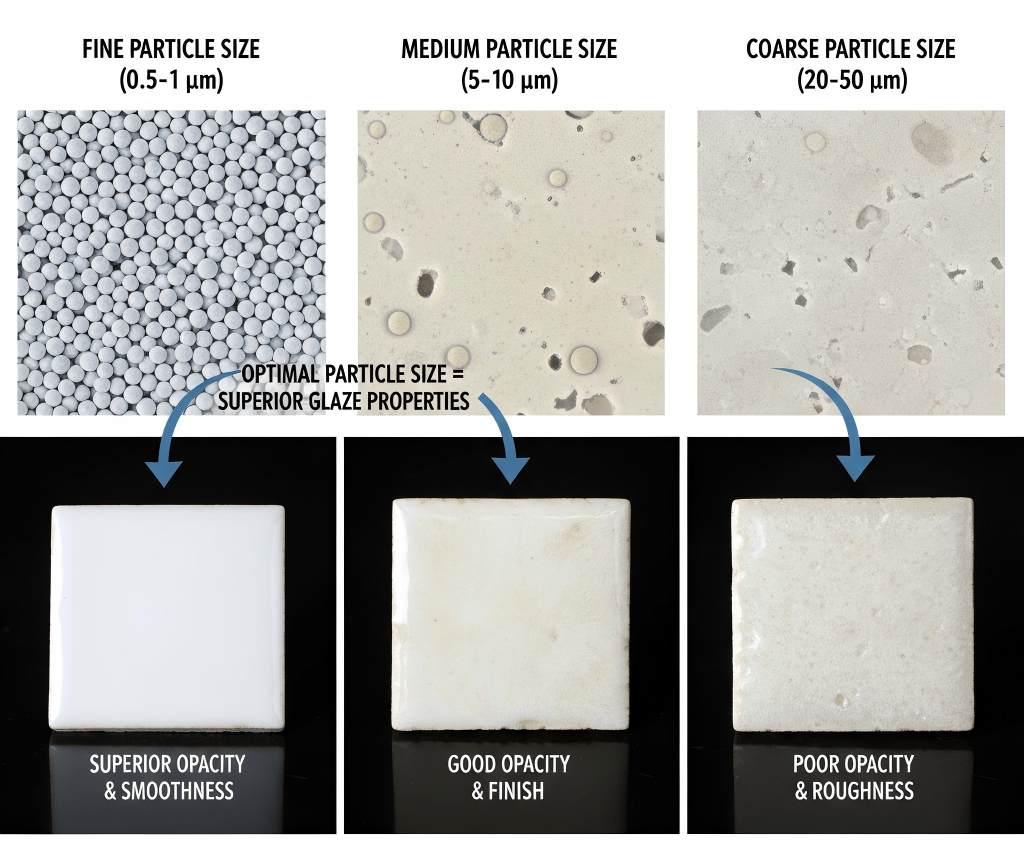
This image illustrates different particle sizes of zirconium silicate, showcasing their significance in achieving optimal glaze properties.
What Techniques Can Enhance Zirconium Silicate Application?
Using zirconium silicate effectively in ceramic glaze formulations requires careful attention to application techniques. Following optimized methods can maximize the benefits this compound offers, ensuring a uniform and high-quality glaze that meets commercial standards.
Recommended Addition Percentages
Finding the correct percentage of zirconium silicate to use is crucial for achieving optimal results. Generally, manufacturers find that a range of 8% to 12% provides a good balance between effectiveness and cost. However, this is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Each production facility may operate under different conditions, and factors such as kiln temperature, firing duration, and the specific compositions of other glaze components can influence the ideal amount. Therefore, we recommend conducting preliminary tests to determine the specific addition rates that yield the best outcomes for your particular setup.
Compatibility with Other Materials
Incorporating zirconium silicate requires a harmonious approach with other glaze components. While zirconium is generally compatible, it can react differently with various materials used in glaze formulations. For instance, colorants or fluxes may alter the intended effects if not properly balanced. Here are a few areas to consider:
- Colorants: Some pigments may not disperse well with zirconium silicate, potentially leading to uneven coloration. Conduct compatibility tests to find the most suitable combinations that will maintain the desired final appearance without producing adverse reactions.
- Fluxes: Various fluxes help improve glaze fluidity during firing. Ensuring that your zirconium-based formulations work effectively with the chosen fluxes is essential for achieving the desired glaze viscosity and appearance.
- Fillers: While fillers can enhance certain aspects of glaze, introducing fillers alongside zirconium silicate may necessitate careful formula adjustments.
Conducting thorough testing on the interactions between zirconium silicate and other materials in your glaze formulation can help mitigate risks and improve consistency.
| Material | Compatibility Type | Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| Colorants | Variable | Reactions possible |
| Fluxes | Generally acceptable | Ensure testing for compatibility |
| Fillers | Limited | May affect viscosity |
Stirring and Mixing Techniques
When incorporating zirconium silicate, thorough mixing is vital. Uneven mixing can lead to unsatisfactory results, such as poor texture or inconsistent whiteness. For optimal results, consider using high-shear mixers, which can ensure uniform dispersion of zirconium silicate within the glaze. Take your time to follow the recommended mixing guidelines for each component to achieve a consistent blend.
Application Methods
Different application techniques may significantly influence the final quality of your glaze. For example, spray application tends to be more effective for achieving even coverage than dip or brush techniques, especially when high opacity is required. Consider your end product’s desired finish when selecting an application method.
Testing for Effects
Lastly, before full-scale production, always prioritize rigorous testing. Create small test batches to observe how varying amounts of zirconium silicate, in combination with other materials, affect the glaze’s performance. Evaluate aspects like whiteness, texture, and durability under actual firing conditions. These test results will guide your full-scale production strategies, helping you precisely formulate the best zirconium silicate applications.
What Are Common Issues and Solutions When Using Zirconium Silicate?
While zirconium silicate is beneficial for boosting glaze whiteness and performance, several common issues can arise during its use. Being proactive in addressing these problems can significantly enhance your manufacturing processes and final product quality.
Why Might the Glaze Still Appear Yellow or Gray?
One of the major challenges faced by many manufacturers is the unexpected yellow or gray appearance of the glaze, despite using zirconium silicate. Several underlying factors could be responsible for this issue:
- Iron Content: A high iron content in raw materials is one of the primary culprits. Iron can impart a yellow hue when fired, counteracting the intended whiteness. Conducting thorough raw material testing before inclusion in your glaze can help identify iron levels and guide decisions on suitable replacements or refinements.
- Kiln Atmosphere: The atmosphere within the kiln during firing can significantly influence the finished product. An oxidizing atmosphere is generally preferred as it allows for brighter colors and prevents undesirable changes. Ensure that your firing conditions are optimal to minimize the risk of glaze discoloration.
- Impurities in Raw Materials: Additional contaminants or impurities can also affect glaze outcomes. Regularly sourcing high-quality, tested materials will help to avoid these issues. Establishing partnerships with reliable suppliers is crucial.
Tackling these problems requires a thorough examination of all materials used in glaze production and strict control over firing conditions.
How to Prevent Pinholes or Bubbles in Glazes?
The appearance of pinholes or bubbles in the glaze can greatly diminish product quality. These issues often arise due to:
- Insufficient Mixing: Unequal dispersion of zirconium silicate can cause air pockets, leading to pinholes or bubbles. Precision in mixing techniques is vital to ensure that all particles, including zirconium silicate, are evenly distributed throughout the glaze.
- Inadequate Venting: During the firing process, gases need to escape efficiently. If the venting is inadequate, bubbles can form in the glaze. Ensure that your kiln allows for adequate gas escape to prevent these imperfections.
- Firing Cycles: The duration and temperature of firing also play crucial roles. Long or overly aggressive firing cycles can affect glaze consistency, leading to bubbles. Reviewing and adjusting firing procedures may be necessary to eliminate this problem.
Implementing thorough testing and quality control measures at each stage of ceramic production will help to prevent these common issues from occurring, enhancing both efficiency and the final quality of your products.

This image illustrates the ceramics manufacturing process, emphasizing the importance of quality in each stage, including the firing of glazes.
Who Are We and Why Choose Our Zirconium Silicate?
When it comes to sourcing high-quality zirconium silicate, our company stands out as a trusted partner.
We supply zirconium silicate sourced from premium materials, ensuring high purity, even particle distribution, and minimal radioactivity. Our rich experience in the ceramics industry allows us to offer tailored solutions designed for the specific needs and challenges faced by manufacturers.
In addition to our product offerings, we pride ourselves on providing exceptional technical support. Our dedicated team is available to assist with formulating and fine-tuning recipes to meet your production goals, ensuring every client achieves optimal results with their ceramic products.
Moreover, we value the feedback and testimonies of our customers. Leading ceramics manufacturers that we collaborate with often highlight improvements in product quality and reductions in waste rates through the effective use of our zirconium compounds.
What Steps Should You Take Next?
As you consider enhancing the whiteness of your ceramic products, a few actionable steps will set you on the right path.
To begin improving the quality of your products, contact us directly. Our technical team is always ready to provide personalized consultations, offering insights based on your unique manufacturing processes.
You may also request free samples to experience the transformative benefits of our zirconium silicate firsthand.
Partnering with Global Industry will empower you to tackle your unique challenges effectively. Let’s work together to improve your ceramic products’ quality and market success.
FAQ Section
Q1: What factors can lead to undesirable glaze coloration with zirconium silicate?
Excessive iron content in raw materials and improper kiln atmospheres can contribute to unwanted color variations. High levels of iron can give a yellow or gray tint to the glaze when fired. Additionally, the absence of an oxidizing atmosphere in the kiln can hinder the brightness of the final product. It is crucial to conduct thorough raw material testing and carefully manage firing conditions to minimize these issues.
Q2: How can I avoid common glaze application issues?
Ensuring thorough dispersion of zirconium components and sufficient venting during firing are key to preventing pinholes and bubbles. Unequal mixing can trap air pockets, resulting in undesirable defects in the glaze. Employing high-shear mixers can help achieve uniformity. Additionally, it’s essential to ensure that gases generated during the firing process are allowed to escape promptly. Regular maintenance and proper kiln operation will enhance overall glazing quality.
Q3: Is zirconium suitable for all ceramic applications?
Zirconium is generally compatible across various ceramic applications; however, testing is recommended for specific formulations and end-use applications. Different products, such as tableware, sanitary ware, and tiles, may have unique requirements. It’s essential to evaluate how zirconium silicate interacts with other materials in your glaze to ensure optimal compatibility and performance before full-scale production.
Q4: What measurement units are used for zirconium purities?
Purity levels of zirconium compounds are commonly discussed in terms of zirconium content percentages, such as 63%, 64%, or 65%. The purity directly influences the performance of the glaze, with higher purity levels typically yielding better results in terms of brightness and opacity. Manufacturers should consider their specific needs and balance costs versus benefits to choose the most suitable zirconium product for their applications.
Q5: How does your zirconium perform compared to competitors?
Our zirconium silicate demonstrates superior performance in enhancing whiteness and physical properties while offering competitive cost-effectiveness. We prioritize high purity and consistent particle sizes, ensuring minimal radioactivity and optimal dispersion in glaze formulations. Many of our clients have reported significant improvements in their products’ visual appeal and durability compared to previous materials, making our zirconium silicate an excellent choice for ceramic manufacturers seeking to improve their product quality and market appeal effectively.