Zircon sand mining can lead to significant environmental challenges that impact local ecosystems. Many purchasing managers and decision-makers are increasingly concerned about these long-term effects. Understanding these impacts is crucial; it helps businesses comply with regulations and adopt responsible practices. This article addresses these concerns by detailing the potential ecosystem consequences of zircon sand mining. It aims to provide actionable insights and practical value that can enhance decision-making. With a credible analysis, this article offers solutions to mitigate negative effects and encourages sustainable management of industrial practices.
What Are the Long-Term Effects of Zircon Sand Mining?
Zircon sand mining has a lasting impact on both the environment and local communities. Mining operations often disrupt habitats, leading to species decline and altering local landscapes. The ecological balance can be endangered as various species struggle to adapt to rapid changes in their environment. So, what does this mean for the ecosystem? Sediments can smother aquatic life, choke off sunlight, and reduce biodiversity.
The effects on biodiversity are profound and multifaceted. Many species may find it difficult to adapt or relocate, putting them at risk of extinction. This loss of genetic diversity can inhibit not only individual species’ resilience against diseases but can also compromise ecosystem stability as a whole.
Understanding these long-term effects of zircon sand mining enables businesses to address environmental responsibilities effectively. For example, heavy machinery used in zircon sand mining can compact soil and destroy vital plant life. This impacts not only ground cover but also the microhabitats that support myriad small organisms, creating a ripple effect throughout the food chain. Ultimately, this can impact larger predators and disrupt the entire ecosystem’s balance.
Assessment of these impacts is crucial for sustainable practices. Companies engaged in zircon sand mining should consistently evaluate how their operations influence ecosystems over time and implement strategies aimed at minimizing disturbances. Developing a robust environmental impact strategy is crucial, promoting transparency and compliance while protecting local ecosystems.
Impact Areas to Consider:
- Biodiversity Loss: Assess the number of species affected in the mining zone, which can help prioritize conservation efforts.
- Soil Structure Disruption: Review how heavy machinery affects soil health to inform rehabilitation strategies.
- Water Quality Declines: Regularly monitor water sources for contamination levels during and after mining operations.
- Community Engagement: Involve local communities in impact assessments related to zircon sand mining activities.
How Does Zircon Sand Mining Affect Local Flora?
Zircon sand mining can severely disrupt local plant life. Plant communities experience reduction due to habitat destruction. You may wonder how this happens. The extraction process often results in the removal of vegetation, which is essential for maintaining soil structure.
The implications extend beyond immediate plant loss. Each species plays a specific role in its ecosystem, from providing food and shelter to influencing soil nutrients. The absence of key species can lead to soil degradation and increased erosion, making recovery significantly harder.
Certain plant species may be directly affected, driven to near extinction in some areas. Disruption can lead to soil erosion, impacting the overall health of the ecosystem. Consider this: a single tree removed can affect countless species. Without the shade and shelter of these trees, other plants may struggle to survive, and animals that rely on them will also be impacted.
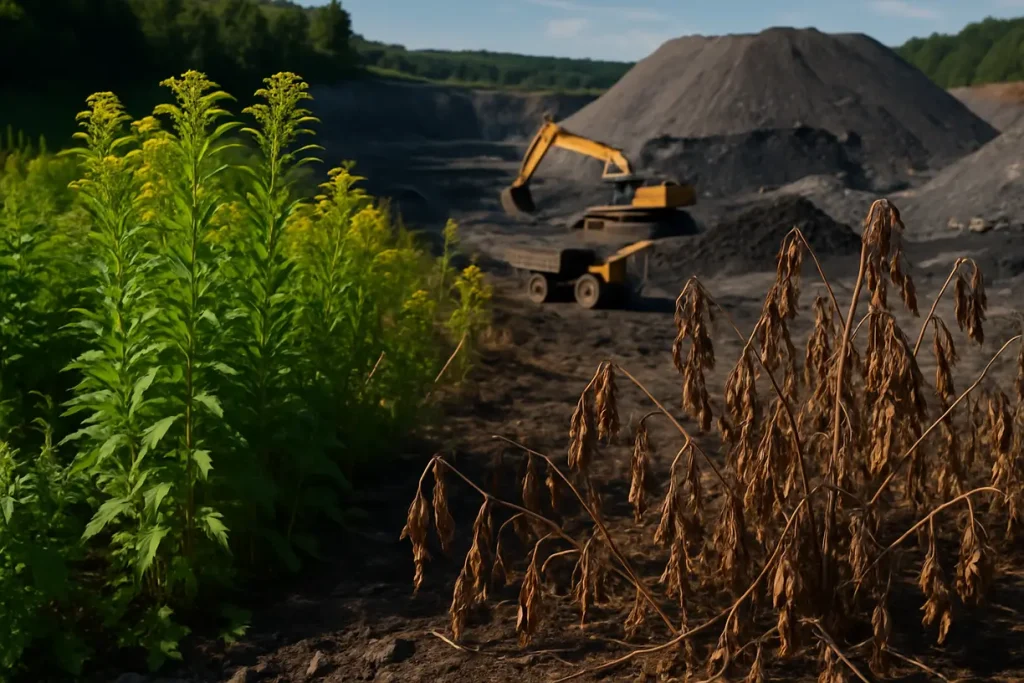

An image capturing local plant life near a mining site showing both healthy and dying vegetation.
Moreover, the introduction of invasive plant species can further complicate recovery. The disturbed soil may become susceptible to opportunistic invaders, which could outcompete native flora. Companies need to implement strategies for restoration, including replanting native species post-mining.
Environmental practices must go beyond compliance, actively working to restore vegetation and ensure ecosystem stability.
| Impact of Zircon Sand Mining on Flora | Details |
|---|---|
| Habitat Loss | Direct removal of vegetation and destruction of habitats |
| Soil Erosion | Disruption of soil leads to erosion and nutrient loss |
| Invasive Species | Potential for invasive plants to dominate the ecosystem |
| Restoration Needs | Importance of replanting native species post-mining |
What Are the Impacts on Local Fauna?
Local fauna face significant threats due to zircon sand mining activities. As the habitat diminishes, animal populations can decline sharply. Is this a cause for concern? Absolutely. Many animals rely on specific plants for their diets or shelter.
Birds, mammals, and reptiles that were once common in the area may begin to disappear as their habitats are destroyed. Let’s break down some specific impacts:
| Impact of Zircon Sand Mining on Fauna | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Habitat Destruction | Loss of homes for local wildlife |
| Population Decline | Decreased numbers due to habitat loss |
| Water Contamination | Harmful effects on aquatic animals and ecosystems |
| Food Chain Disruption | Imbalances in the ecosystem affecting biodiversity |
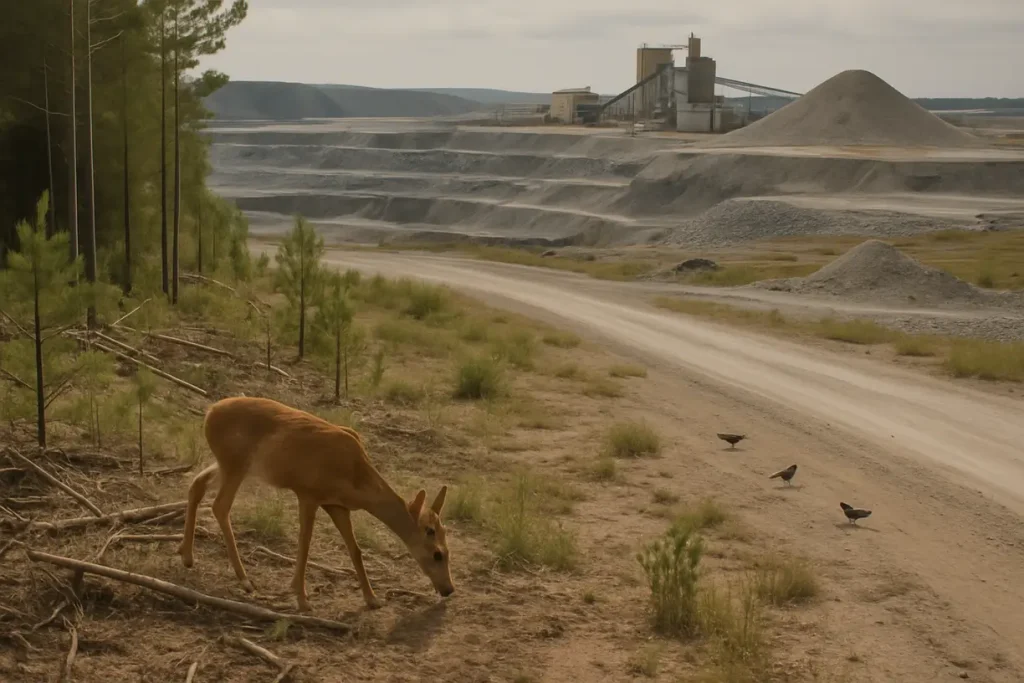

This image illustrates local wildlife, emphasizing the habitat disruptions caused by mining activities.
Water contamination is another serious issue. Chemicals and sediments from mining can enter waterways, harming aquatic life. Many fish and amphibians are sensitive to water quality changes, and their decline can further affect local ecosystems.
Companies must recognize these impacts and take appropriate measures to mitigate them. Engaging in habitat conservation and responsible mining practices could pave the way for healthier ecosystems. Regular monitoring and assessment of local fauna can help in tracking the effectiveness of conservation measures.
How Does Water Quality Change Due to Mining?
Water quality deteriorates as a result of zircon sand mining. Sediments and chemicals enter local water systems, leading to significant environmental issues. So, what’s at stake? Clean water is vital for all life forms, both terrestrial and aquatic.
Sediment runoff can cause turbidity, which interferes with photosynthesis in aquatic plants. Have you thought about what this means? Reduced plant life impacts the entire aquatic food web. Fish and other organisms that rely on plants for oxygen and nutrition could struggle to survive.
The implications are serious, impacting both wildlife and human populations. Poor water quality can lead to increase in health issues among nearby communities, including gastrointestinal illnesses and long-term developmental issues in children.
Moreover, toxic substances can contaminate drinking water sources, posing health risks to local communities. The potential for increased disease rates also rises.
Companies involved in mining must prioritize water management practices that reduce contamination risks. Implementing robust water monitoring systems is essential. These systems should aim to detect changes in water quality and provide solutions to tackle contamination.
| Factors Influencing Water Quality in Mining Areas | Effects |
|---|---|
| Sediment Runoff | Turbidity reducing photosynthesis in aquatic plants |
| Chemical Contaminants | Potential health risks to humans and local fauna |
| Increased Disease Rates | Declining public health due to contaminated water |
| Reduced Fish Populations | Disruption in aquatic food webs affecting ecosystems |
What Are the Soil Health Implications?
The health of soil suffers significantly due to zircon sand mining. The process disrupts the natural structure of the soil, making it less fertile and more prone to erosion. Have you considered the long-term effects of this disruption? It can take years for soil to recover after mining.
Soil contamination with heavy metals and other toxins is another concern. Contaminated soil can negatively affect plants and animals that depend on it for food. How can this contamination be mitigated effectively?
- Regular Soil Testing: Monitoring soil for contaminants can help identify issues before they escalate.
- Organic Remediation: Techniques such as composting and bioremediation can help restore soil health.
The removal of topsoil during mining can lead to a significant decline in soil fertility. The nutrient profile is altered, which affects everything from plant growth to the surrounding fauna that rely on those plants.
Reclamation practices are vital to return soil health to its natural state following mining operations. Strategies might include soil testing and the addition of organic matter to rebuild soil structure.
Companies must integrate soil health management into their broader environmental policies to promote sustainable mining practices.
| Soil Health Impact Factors | Potential Implications |
|---|---|
| Soil Erosion | Loss of topsoil and reduced fertility |
| Soil Contamination | Toxic effects on plant growth and animal health |
| Recovery Time | Years required for soil to return to health |
| Restoration Strategies | Testing, organic amendments, and vegetation replanting |
How Can Communities Mitigate Adverse Effects?
Local communities play a pivotal role in mitigating the adverse effects of zircon sand mining. Community involvement can significantly enhance awareness and action. So, what steps can be taken?
Education programs are essential to inform residents about the potential impacts of mining. These programs can address various aspects, including:
- Workshops: Educating community members on environmental stewardship.
- Local Initiatives: Establishing networks for monitoring ecological changes.
Communities can engage with mining companies to advocate for responsible practices. This may include setting expectations for environmental standards and rehabilitation efforts.
Collaborating with environmental organizations can also bolster advocacy efforts. Partnerships can lead to useful initiatives for monitoring environmental health. These measures promote accountability and long-term sustainability.
Communities should actively participate in shaping mining policies. Engaging with local governments ensures that community voices are heard. Effective communication channels can facilitate these discussions and lead to better outcomes.
| Community Mitigation Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Educational Programs | Increased awareness about environmental impacts |
| Collaboration with Mining Companies | Advocacy for responsible mining practices |
| Partnerships with Environmental Organizations | Effective monitoring and accountability |
| Active Participation in Policy Making | Empowering local voices in decision-making processes |
What Regulatory Measures Are in Place?
Regulatory measures for zircon sand mining are critical in protecting local ecosystems and ensuring that mining activities take place responsibly. Various regulations exist at both national and international levels aimed at minimizing environmental impacts associated with mining. Understanding these regulations is vital for mining companies to operate within legal frameworks and maintain their social license to operate.
One of the primary measures involves requiring comprehensive environmental assessments prior to the granting of mining permits. These assessments evaluate the potential impacts on flora, fauna, and water quality, serving as a crucial step in identifying risks associated with mining operations. Companies must submit detailed reports outlining how they plan to mitigate potential environmental damages before they can commence mining activities.
Moreover, effective enforcement of these regulations can vary by region, leading to disparities in environmental protection. In areas with insufficient oversight, mining activities may result in significant ecological degradation, highlighting the need for improved governance and compliance mechanisms. To strengthen environmental protections, regulatory bodies may introduce more stringent compliance requirements, demanding regular impact assessments throughout the mining lifecycle to ensure ongoing monitoring of environmental health.
Transparency is also an essential component of regulatory frameworks. Companies are encouraged to disclose their mining activities and environmental consequences, fostering trust with local communities and regulatory authorities. Public reporting of environmental performance metrics allows stakeholders to stay informed about mining impacts and the effectiveness of mitigation strategies.
In addition to compliance with existing regulations, advocacy for the improvement of mining laws is necessary to address gaps and promote stricter enforcement. Businesses that prioritize regulatory compliance not only contribute to environmental stewardship but also enhance their marketability by demonstrating a commitment to sustainable practices.
Key considerations related to regulations include:
- Environmental Assessments: Evaluate potential impacts before mining begins, establishing baseline conditions for ecosystems.
- Compliance Requirements: Ensure adherence to environmental standards that protect biodiversity and water quality throughout mining operations.
- Public Disclosure: Foster transparency about mining activities, encouraging open communication with local communities regarding potential impacts.
- Advocacy for Stronger Regulations: Promote better oversight and accountability in the mining sector to minimize ecological footprints and uphold social responsibilities.
By understanding and adhering to these regulatory measures, companies can engage in sustainable mining practices that benefit both their operations and the health of local ecosystems. Ultimately, responsible engagement with regulatory frameworks not only safeguards natural resources but also supports the long-term viability of the zircon mining industry.ter enforcement. Companies that prioritize compliance not only protect ecosystems but also enhance their marketability.
How Does Zircon Mining Impact Indigenous Communities?
Zircon mining impacts indigenous communities directly and profoundly. Many indigenous groups rely on land for cultural practices, sustenance, and well-being. What are the implications for these communities?
Mining activities can lead to displacement and loss of traditional lands. Such disruptions jeopardize cultural identity and traditional ways of life. Community ties to the land run deep, making these losses particularly devastating.
Additionally, economic inequality can arise as the benefits of mining may not reach local populations. Local jobs often go to individuals from outside the community, diminishing economic opportunities for residents.
Engagement is key. Mining companies must work closely with indigenous communities to create partnership agreements that respect traditions and protect rights.
It’s vital to ensure that these agreements include:
- Cultural Preservation: Guaranteeing the protection of culturally significant sites.
- Economic Opportunities: Creating job training programs for local residents.
Responsibility and respect for indigenous rights are crucial in fostering healthier relationships and ensuring that mining practices contribute positively to all stakeholders involved.
| Impacts on Indigenous Communities | Consequences |
|---|---|
| Displacement from Traditional Lands | Loss of cultural identity and practices |
| Economic Inequality | Limited job opportunities for local populations |
| Impacts on Health and Well-Being | Decreased quality of life due to environmental degradation |
| Partnership Agreements | Need for responsible engagement and benefit sharing |
What Are Successful Reclamation Strategies?
Reclamation is essential for restoring ecosystems after zircon sand mining. Successful strategies can significantly enhance recovery of the land. What methods yield the best outcomes?
Active replanting of native species often proves effective. Establishing vegetation can stabilize soil, improve water retention, and foster biodiversity.
Case studies of successful reclamation efforts show the importance of tailored approaches. For example, some companies have employed techniques like contour planting, which helps manage erosion. Others have implemented wetland restoration to create new habitats.
Regular monitoring and ongoing maintenance are crucial. Keeping tabs on the reclaimed areas helps identify issues early and ensures adherence to best practices.
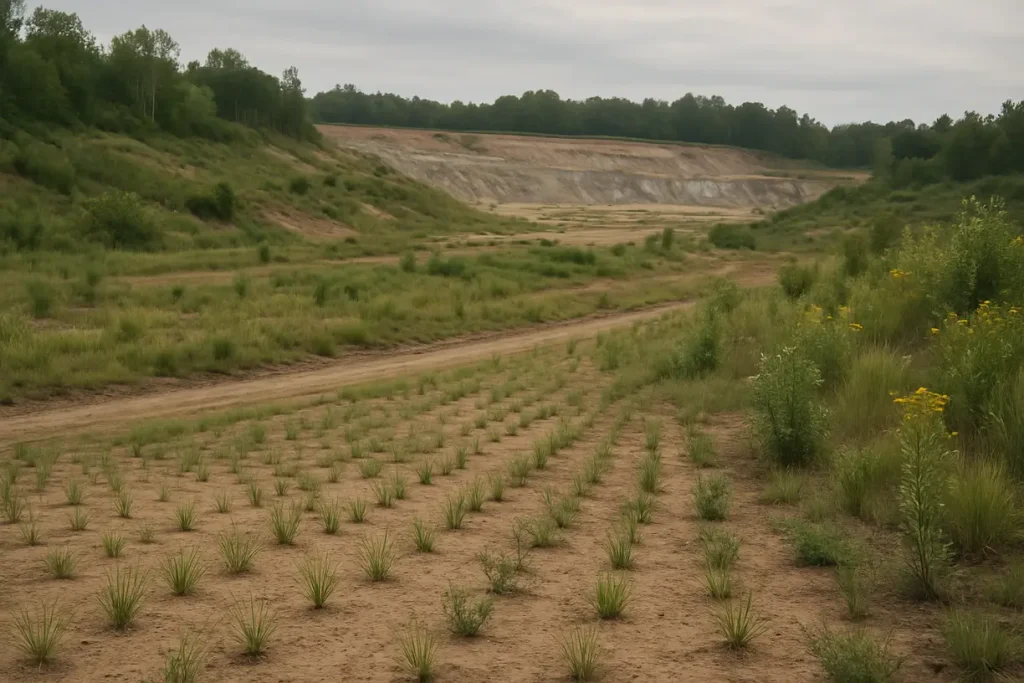

This image depicts a reclaimed landscape, illustrating the successful restoration efforts after mining activities.
Best Practices for Reclamation:
- Soil Assessment: Regularly test soil to check recovery progress.
- Native Species Selection: Choose plants that are native to the area and well-suited for the local climate.
- Community Involvement: Engage local communities in reclamation efforts, providing educational opportunities.
Integrating these strategies into mining operations promotes sustainability and protects ecosystems long-term.
| Reclamation Strategies | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Native Species Replanting | Restores habitats and fosters biodiversity |
| Contour Planting | Reduces soil erosion and improves water management |
| Wetland Restoration | Creates new habitats for aquatic life |
| Regular Monitoring and Maintenance | Ensures effective recovery of ecosystems |
How Can B2B Companies Benefit from Sustainable Practices?
Sustainable mining practices offer several advantages for B2B companies. Why should businesses care? Implementing responsible methods can lead to improved reputations and customer loyalty.
A focus on sustainability can enhance a company’s marketability. Consumers are increasingly concerned about environmental responsibility. Companies seen as eco-friendly often attract more business.
Financial benefits may arise from reduced regulatory risks and compliance. Companies investing in sustainable practices can experience lower operational costs due to improved efficiencies.
Moreover, fostering partnerships with environmental organizations adds credibility. These initiatives can enhance brand recognition and lead to more contracts and collaborations.
Incorporating sustainable practices should be a long-term business strategy.
Key Advantages of Sustainable Mining Practices:
| Benefits of Sustainable Practices | Examples |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Reputation | Attracts environmentally-conscious customers |
| Reduced Regulatory Risks | Minimizes the potential for costly compliance issues |
| Improved Operational Efficiency | Lower operational costs through effective resource management |
| Partnerships with Environmental Organizations | Builds credibility and enhances brand recognition |
Conclusion
In summary, zircon sand mining presents significant and long-lasting implications for local ecosystems. The loss of flora and fauna, alongside deteriorating water quality, highlights the urgent need for responsible practices. Not only do these practices protect biodiversity, but they also enhance the reputation and sustainability of businesses involved in the industry.
By implementing effective strategies and engaging local communities, companies can achieve both environmental responsibility and economic viability. Global Industry encourages businesses to prioritize sustainable methods that foster ecosystem health and long-term benefits. For further insights or to develop a tailored sustainability strategy, please reach out to us for a consultation on best practices in zircon sand mining management. Together, we can build a more sustainable future for our planet and the communities we serve.
FAQ Section
Q1: What is zircon sand mining?
Zircon sand mining refers to the extraction of zircon, a mineral valued for its use in ceramics, electronics, and as a gemstone. This process usually involves open-pit mining techniques, which can have significant environmental impacts.
Q2: What are the primary environmental concerns?
Key environmental concerns include habitat destruction, water contamination from mining runoff, and loss of biodiversity as various species are displaced. Additionally, changes in soil structure can lead to long-term ecological imbalances.
Q3: How can local populations be involved in monitoring impacts?
Local communities can actively engage in monitoring through educational programs, workshops, and partnerships with environmental organizations. By participating in data collection and impact assessments, locals can gain knowledge and advocate for responsible mining practices.
Q4: Are there successful case studies of restoration?
Yes, several regions have implemented successful reclamation projects where ecosystems have been restored post-mining. These projects often involve replanting native species and restoring habitats, showcasing the potential for land recovery when proper practices are employed.
Q5: What role do businesses play in promoting sustainability in mining?
Businesses can adopt sustainable practices by incorporating eco-friendly technologies, enhancing supply chain transparency, and actively collaborating with environmental organizations. By prioritizing sustainability, they not only minimize their environmental footprint but also meet increasing consumer demands for responsible sourcing.