The Challenge of Sourcing Zirconium in 2025
Keeping pace with the dynamic global zirconium market is challenging. Sourcing Zirconium Dioxide (ZrO₂), zircon sand, and advanced ceramic components in 2025 requires current knowledge of:
- Supply chain developments
- Price volatility patterns
- Emerging applications in critical sectors
Without this understanding, your procurement strategy risks higher costs, supply disruptions, or missed opportunities in sectors like batteries, semiconductors, green steelmaking, 5G, and medical devices.
Why This Matters to Your Business
Consider these scenarios:
- You need high-purity 99.9%+ ZrO₂ for next-gen batteries or semiconductors but lack key supplier criteria
- You’re sourcing zircon sand for green steelmaking while needing cost-saving alternatives
- Your access to ceramic components for 5G or medical applications is limited by insufficient knowledge of manufacturer evaluation
Geopolitical factors add complexity, impacting both supply and pricing. The rapid market changes can make strategic purchasing decisions difficult without proper guidance.
Your Comprehensive Solution
This 2025 Global Zirconium Trends and Supply Guide offers clarity and actionable insights across the entire zirconium value chain:
- Market Overview
- Zirconium supply chain updates
- 2025 price and production forecasts
- Geopolitical impacts on supply
- High-Purity Zirconia Sourcing
- 99.9%+ ZrO₂ for batteries and semiconductor applications
- Nano ZrO₂ for advanced 3D printing
- Supplier selection criteria for specialized materials
- Zircon Sand Procurement
- New applications in green steelmaking
- Cost-saving alternatives
- Quality and logistics optimization
- Advanced Ceramic Components
- 5G and medical applications
- Manufacturer evaluation techniques
- Automotive industry case study
- Strategic Buying Guide
- Managing price fluctuations
- Understanding certification requirements
- Obtaining samples and quotes effectively
Transform your zirconium procurement from reactive to proactive, ensuring quality, cost-effectiveness, and supply security.
Foundational Analysis: Understanding Key Trends in the 2025 Zirconium Supply Chain
The 2025 global zirconium market is dynamic. Understanding supply chain updates, price forecasts, and geopolitical impacts is crucial for effective procurement.
Demand for zircon sand, ZrO₂, and ceramic components is shaped by:
- Technological advancements
- Sustainability initiatives
- Economic shifts
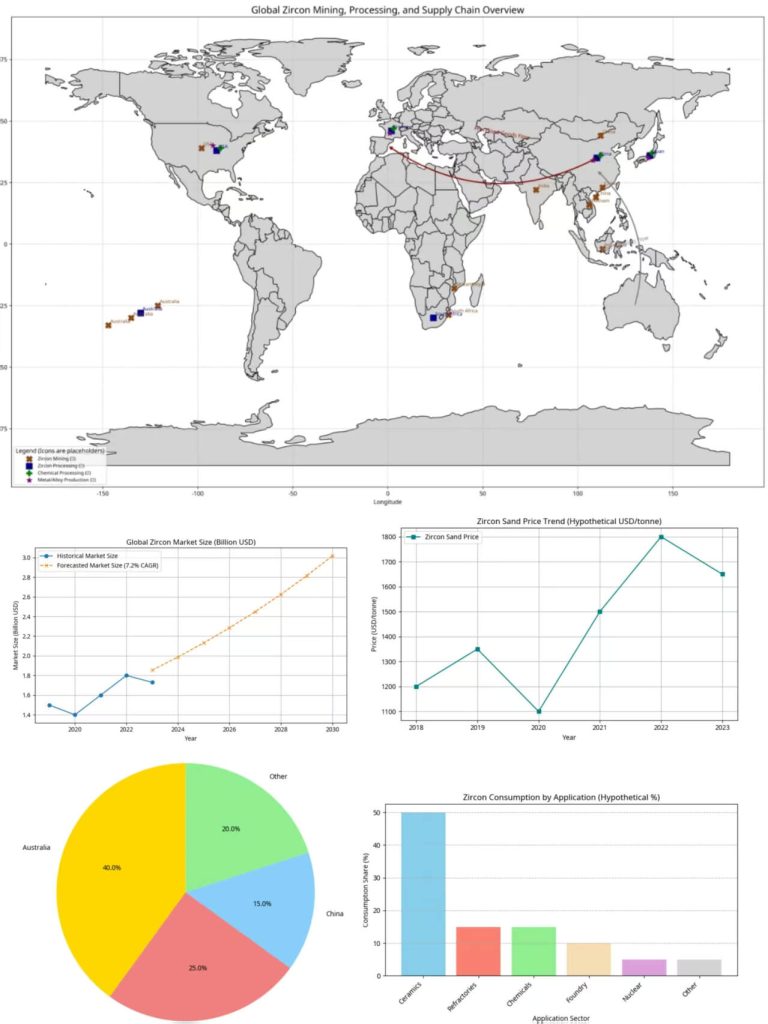
Electrification and renewable energy adoption boost demand for specialized ZrO₂ in batteries and fuel cells, while traditional ceramic and refractory markets remain key consumers. According to Mordor Intelligence, the global zirconium market is expected to reach 1.76 million tons in 2025 and grow at a CAGR of 4.30% to reach 2.18 million tons by 2030.
Zirconium Supply Chain Updates
Staying current with zirconium supply chain developments is vital in 2025. The journey from zircon ore to finished high-purity ceramic components involves multiple stages:
Mining and Extraction:
- Zircon (ZrSiO₄) is the primary source, often co-produced with heavy mineral sands
- Major producing regions: Australia, South Africa, USA, Mozambique, Senegal, Indonesia
- Disruptions (weather, labor, regulations, resource depletion) impact global supply
Processing and Refining:
- Raw zircon sand is processed, graded, and shipped globally
- Downstream processors (mainly in China, but also Europe and India) convert it to:
- Zirconium chemicals
- ZrO₂ of varying purities
- Zirconium metal
- Processing facilities represent critical choke points in the supply chain
Logistics Considerations:
- Shipping, port capacities, and inland transport affect availability
- Disruptions like port congestion and container shortages impact costs and lead times
- Supply chain transparency and ethical sourcing requirements are increasing
| Supply Chain Stage | Key Factors to Monitor in 2025 | Potential Impact on Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| Mining & Extraction | Output from major producing countries; new mine developments; depletion rates | Fluctuations in raw zircon sand availability and base price |
| Zircon Processing | Beneficiation plant capacities; quality grades produced; export logistics | Availability of specific zircon grades; regional price differences |
| Chemical Processing | ZrO₂ production capacities; energy costs; environmental regulations | Availability and cost of zirconia powders and chemicals |
| High-Purity Refining | Capacity for 99.9%+ ZrO₂; purification technology advancements | Availability and pricing for battery-grade and electronics-grade ZrO₂ |
| Logistics | Shipping rates; port congestion; container availability; trade routes | Lead times, freight costs, and overall landed cost |
| Regulatory & ESG | Environmental regulations; labor laws; conflict mineral concerns | Compliance requirements; demand for supply chain transparency |
Effective supply chain monitoring requires:
- Continuous market research
- Strong supplier relationships
- Alternative sourcing strategies
- Understanding of price transmission mechanisms
High-Purity Zirconia (HPZ): Advanced Applications and Sourcing Strategies
High-Purity Zirconia (HPZ), with purities exceeding 99.9% ZrO₂, is crucial for advanced technologies due to its unique properties:
- Ionic conductivity
- Thermal stability
- Chemical inertness
Producing HPZ involves sophisticated chemical purification processes, contributing to its higher cost compared to standard grades.

99.9%+ ZrO₂ for Batteries & Chips
The demand for ultra-high purity ZrO₂ is surging in two critical sectors:
Battery Applications:
- Used in next-generation solid-state lithium-ion batteries
- Functions as solid electrolyte material or electrode coating
- Provides high ionic conductivity (when appropriately doped)
- Enhances battery safety, cycle life, and energy density
- Requires extremely low impurity levels (<100 ppm of Fe, Si, Al, Na)
Semiconductor Industry:
- Used in plasma etching equipment components
- Applied in wafer handling systems
- Offers resistance to corrosive environments
- Provides excellent wear resistance and dielectric properties
- Smaller chip feature sizes demand extreme material purity
Sourcing Considerations:
- Partner with specialized suppliers having robust quality control
- Request detailed Certificates of Analysis (CoAs)
- Verify impurity levels down to parts per million (ppm)
- Ensure consistent particle size distribution and morphology
- Conduct thorough supplier audits
Nano ZrO₂ for 3D Printing
Nanostructured zirconia powders are revolutionizing additive manufacturing of complex ceramic parts. With particle sizes typically below 100 nanometers, these materials offer significant advantages in 3D printing processes like stereolithography, digital light processing, or binder jetting. The benefits include:
- Higher sintered densities
- Finer microstructures
- Improved mechanical properties
- Ability to create intricate geometries
Key Applications:
- Dental (crowns, bridges, implants)
- Medical (surgical guides, bone scaffolds)
- Luxury goods (watch components)
- Chemical industry (micro-reactors, catalyst supports)
When sourcing nano-zirconia for 3D printing, critical factors include particle size distribution, agglomeration state, purity, phase stability, and compatibility with specific printing technologies. Suppliers must demonstrate excellent control over synthesis and powder processing to ensure the batch-to-batch consistency that reliable 3D printing outcomes demand.
Supplier Selection Criteria
When sourcing High-Purity Zirconia, evaluate potential suppliers on these key factors:
- Technical Capability and Expertise
- Advanced manufacturing processes
- R&D capabilities
- Ability to meet exact specifications
- Track record in your application area
- Quality Management Systems
- ISO 9001 certification
- Industry-specific certifications (ISO 13485, IATF 16949)
- Process control and traceability
- Analytical Capabilities
- Detailed Certificates of Analysis
- In-house advanced analytical equipment
- Verification through independent testing
- Consistency and Reliability
- Demonstrated batch-to-batch consistency
- Reliable lead times
- Capacity to meet volume requirements
- Total Cost of Ownership
- Quality and consistency benefits
- Technical support value
- Impact on your process yields
- Ethical Sourcing and Sustainability
- Environmental impact
- Responsible sourcing practices
- Long-term sustainability
Zircon Sand: Market Intelligence & Emerging Uses
Zircon Sand (ZrSiO₄) remains fundamental in the zirconium value chain, with applications extending beyond traditional uses in ceramics and foundries.

New Uses in Green Steelmaking
Zircon Sand is finding exciting applications in environmentally friendly steel production. As the steel industry transitions toward more sustainable practices, high-performance refractories become increasingly important. Zircon’s exceptional properties make it valuable for specialized furnace components:
- High melting point (approximately 2,550°C) for extreme temperature resistance
- Low thermal expansion to minimize cracking during temperature cycles
- Excellent corrosion resistance against molten metal and slag
- Good thermal shock resistance for durability in dynamic conditions
These properties make zircon ideal for specialized furnace linings, slide gates, and mold coatings for high-quality steel casting. The material contributes to “green” steelmaking by enabling more efficient, lower-emission production processes and improving the energy efficiency of refractory linings.
Cost-Saving Alternatives
While zircon offers unique properties, its price volatility has prompted exploration of alternatives. Finding direct substitutes is challenging due to zircon’s unique combination of refractoriness, chemical inertness, and opacity in ceramic applications.
For foundry applications, materials like chromite sand, olivine sand, or synthetic sands might be considered, though each has different thermal properties and health considerations. In ceramics, alternative opacifiers or formulation adjustments can reduce zircon content, often with compromises in whiteness or opacity.
Evaluating alternatives requires understanding your application’s critical performance requirements and conducting rigorous testing. Consider not just the material price but the total cost of use, including processing requirements, energy consumption, and product lifespan.
Buying Tips: Quality & Logistics
Effective procurement of Zircon Sand requires attention to both quality and logistics:
Quality Specifications:
- Define critical parameters: ZrO₂+HfO₂ content, Fe₂O₃, TiO₂, Al₂O₃ levels
- Specify particle size distribution requirements
- Consider radioactivity levels (NORMs)
- Provide detailed specifications to suppliers
Supplier Evaluation:
- Source from reputable miners or processors
- Request Certificates of Analysis for each batch
- Consider independent third-party testing
- Understand mining sources and processing methods
Pricing Strategies:
- Track benchmark prices from major producers
- Negotiate terms balancing competitiveness and security
- Consider a mix of spot and contract purchases
- Monitor market trends regularly
Logistics Optimization:
- Evaluate shipping options (bulk vessel, containers)
- Optimize inland transportation
- Ensure proper packaging to prevent contamination
- Consider supplier proximity to minimize costs
Inventory Management:
- Maintain appropriate buffer stock
- Align inventory strategy with consumption rate
- Balance working capital constraints with supply security
Ceramic Components: 5G, Medical, Auto Applications & Sourcing
Sourcing advanced Ceramic Components made from zirconia presents unique challenges due to complex manufacturing processes and critical performance requirements.

5G & Medical Applications
Zirconia ceramics play pivotal roles in both telecommunications and healthcare:
5G Applications:
- Resonators and filters
- Substrates for high-frequency devices
- Packaging for RF components
- Benefits include low dielectric loss, high thermal conductivity, and mechanical robustness
Medical Applications:
- Dental implants, crowns, and bridges (biocompatible YSZ)
- Orthopedic components (hip and knee replacements)
- Surgical instruments
- Key advantages: biocompatibility, aesthetics, strength, and wear resistance
Sourcing Considerations:
- Identify suppliers with specific expertise in these fields
- Verify relevant certifications (FDA approval, ISO 13485)
- Ensure controlled manufacturing processes
- Require thorough material characterization
Evaluating Manufacturers
Assessment of zirconia component manufacturers should consider:
- Technical Expertise
- Experience with zirconia processing
- Advanced forming techniques capability
- Controlled sintering processes
- Precision finishing capabilities
- Quality Management
- Relevant certifications (ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF 16949)
- In-process quality control procedures
- Final inspection protocols
- Material Control
- Incoming powder quality verification
- Full traceability systems
- Consistent material properties
- Engineering Support
- Design assistance capabilities
- Co-engineering opportunities
- R&D investments
- Production Capacity
- Current and future volume capabilities
- Lead time reliability
- Scalability options
- Business Stability
- Financial health
- Industry reputation
- Long-term partnership potential
- Cost Competitiveness
- Total cost of ownership perspective
- Quality and reliability factors
- Value-added services
Automotive Case Study
Oxygen sensors (lambda sensors) illustrate the demands placed on zirconia components:
Application Context:
- Critical for controlling fuel injection and reducing emissions
- Sensing element made from Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ)
- Must operate reliably in harsh environments (800-900°C)
- Exposed to thermal shocks, vibrations, and corrosive gases
Sourcing Requirements:
- Precise material specifications (yttria content, particle size, purity)
- Complex manufacturing processes (tape casting, extrusion, sintering)
- IATF 16949 quality certification
- Extensive testing protocols
- High-volume production capabilities with low defect rates
Key Lessons:
- Success requires deep partnerships with technically proficient manufacturers
- Quality, reliability, and cost targets must be balanced
- Principles apply to other industries, including 5G and medical applications
Zirconium Buying Guide: Price, Certifications, Samples & Quotes
Navigating the 2025 zirconium market requires a robust procurement strategy covering price management, certification compliance, and supplier engagement.
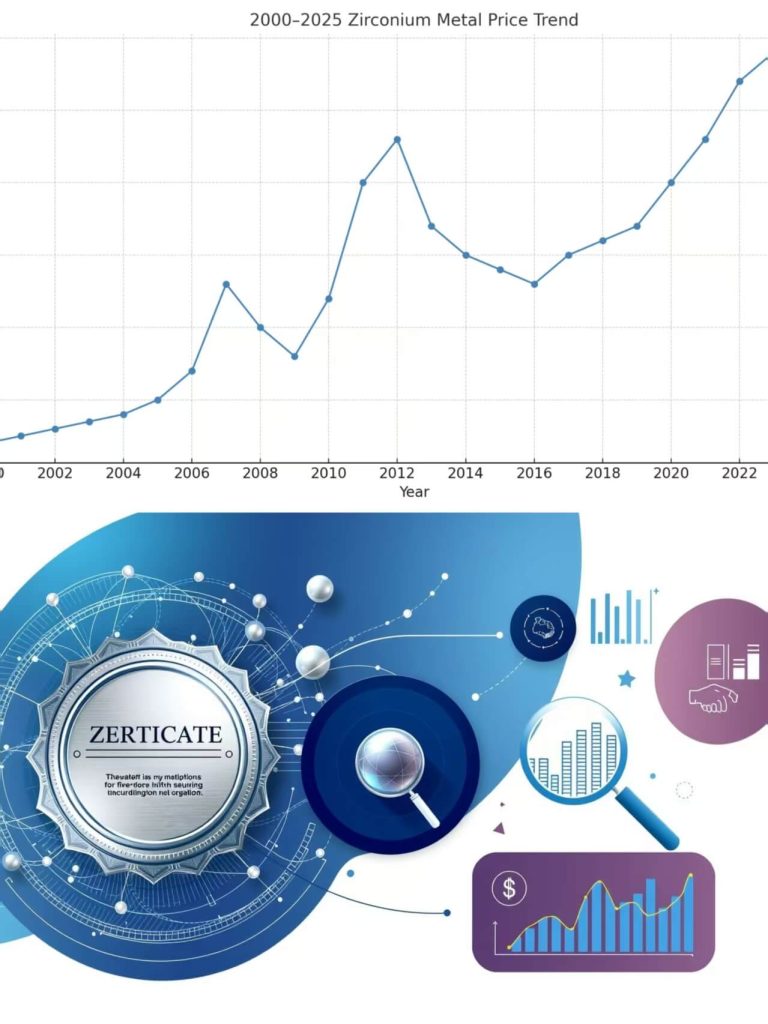
Managing Price Fluctuations
Zirconium material prices can be volatile due to multiple factors:
- Global supply/demand shifts
- Mining output changes
- Currency movements
- Energy costs
- Freight rates
- Macroeconomic trends
Effective Management Strategies:
- Market Intelligence
- Invest in reliable market information sources
- Analyze trends to develop price forecasts
- Monitor key producing regions
- Strategic Sourcing
- Explore longer-term contracts (6-12+ months)
- Consider fixed or indexed pricing options
- Implement price caps or collars where possible
- Diversify your supplier base
- Inventory Management
- Maintain appropriate safety stock
- Adjust inventory levels based on market forecasts
- Balance holding costs against supply risk
- Value Engineering
- Optimize material usage efficiency
- Reduce waste in processing
- Qualify alternative grades for non-critical applications
Certification Requirements
Understanding and navigating certification requirements is essential in the zirconium supply chain. Material certifications verify chemical composition, physical properties, particle characteristics, and other critical parameters. Process certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 14001, ISO 13485, and IATF 16949 provide assurance of quality management systems appropriate to different industries.
End-use specific requirements might include:
- FDA compliance for medical applications
- RoHS compliance for electronics
- REACH compliance for European markets
- Industry-specific standards for automotive or aerospace
Maintaining organized certification records, implementing regular supplier audits, establishing clear specification requirements, and developing testing protocols for verification are all important aspects of certification management.al supplies while optimizing costs and ensuring quality requirements are met.
FAQ Section
Q1: How will the 2025 zirconium market differ from previous years?
The 2025 market shows increased segmentation between standard and high-purity grades. While traditional applications in ceramics and refractories remain important, new high-growth sectors like batteries, semiconductors, and green steelmaking are driving demand for specialized grades. Supply chains are more regionalized due to geopolitical factors, with greater emphasis on securing critical materials. Price volatility has increased, making strategic sourcing more important than ever.
Q2: What are the key quality parameters to consider when sourcing high-purity ZrO₂?
When sourcing high-purity ZrO₂, focus on: total ZrO₂+HfO₂ content (typically >99.9%); specific impurity levels (particularly Fe, Si, Al, Na, Ca); particle size distribution and morphology; surface area; phase composition; and agglomeration state. Request detailed Certificates of Analysis showing trace element analysis down to ppm levels. For battery and semiconductor applications, additional parameters like ionic conductivity or specific surface chemistry may be critical.
Q3: How can I verify supplier claims about zirconium material quality?
Implement a multi-step verification process: request comprehensive Certificates of Analysis with each shipment; conduct regular third-party testing through accredited laboratories; perform incoming quality control testing on critical parameters; visit supplier facilities to audit their quality control processes; and gradually build trust through consistent quality over multiple deliveries. For critical applications, consider testing the material in your actual production process before full implementation.
Q4: What supply chain risks should I monitor for zirconium materials in 2025?
Key risks include: concentration of mining in a few countries (Australia, South Africa, Senegal); processing bottlenecks, particularly in China; energy availability and cost impacts on production; shipping disruptions affecting global logistics; regulatory changes regarding mining or processing; and increasing ESG requirements affecting supplier operations. Develop a risk matrix specific to your supply chain, with mitigation strategies for each identified risk factor.
Q5: How can I balance cost and quality considerations when sourcing zirconium products?
Take a total cost of ownership approach rather than focusing solely on unit price. Consider how material quality affects your production yields, product performance, and customer satisfaction. Segment your applications based on criticality—use highest quality for critical applications while finding cost-effective alternatives for less demanding uses. Develop partnerships with key suppliers that balance quality assurance with competitive pricing, potentially through longer-term agreements that benefit both parties.